mirror of
https://github.com/puppeteer/puppeteer
synced 2024-06-14 14:02:48 +00:00
This patch drops the markdown-toc module and instead rolls out our own simple markdown table-of-contents generator. As a side effect, it fixes links to `page.$` and `page.$$`.
2963 lines
138 KiB
Markdown
2963 lines
138 KiB
Markdown
##### Released APIs: [v1.4.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.4.0/docs/api.md) | [v1.3.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.3.0/docs/api.md) | [v1.2.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.2.0/docs/api.md) | [v1.1.1](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.1.1/docs/api.md) | [v1.1.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.1.0/docs/api.md) | [v1.0.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v1.0.0/docs/api.md) | [v0.13.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.13.0/docs/api.md) | [v0.12.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.12.0/docs/api.md) | [v0.11.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.11.0/docs/api.md) | [v0.10.2](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.10.2/docs/api.md) | [v0.10.1](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.10.1/docs/api.md) | [v0.10.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.10.0/docs/api.md) | [v0.9.0](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/v0.9.0/docs/api.md)
|
|
|
|
# Puppeteer API <!-- GEN:version -->Tip-Of-Tree<!-- GEN:stop-->
|
|
|
|
<!-- GEN:empty-if-release -->
|
|
> Next Release: **June 7, 2018**
|
|
<!-- GEN:stop -->
|
|
|
|
|
|
##### Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
<!-- GEN:toc -->
|
|
- [Overview](#overview)
|
|
- [Environment Variables](#environment-variables)
|
|
- [class: Puppeteer](#class-puppeteer)
|
|
* [puppeteer.connect(options)](#puppeteerconnectoptions)
|
|
* [puppeteer.createBrowserFetcher([options])](#puppeteercreatebrowserfetcheroptions)
|
|
* [puppeteer.defaultArgs()](#puppeteerdefaultargs)
|
|
* [puppeteer.executablePath()](#puppeteerexecutablepath)
|
|
* [puppeteer.launch([options])](#puppeteerlaunchoptions)
|
|
- [class: BrowserFetcher](#class-browserfetcher)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.canDownload(revision)](#browserfetchercandownloadrevision)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.download(revision[, progressCallback])](#browserfetcherdownloadrevision-progresscallback)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.localRevisions()](#browserfetcherlocalrevisions)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.platform()](#browserfetcherplatform)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.remove(revision)](#browserfetcherremoverevision)
|
|
* [browserFetcher.revisionInfo(revision)](#browserfetcherrevisioninforevision)
|
|
- [class: Browser](#class-browser)
|
|
* [event: 'disconnected'](#event-disconnected)
|
|
* [event: 'targetchanged'](#event-targetchanged)
|
|
* [event: 'targetcreated'](#event-targetcreated)
|
|
* [event: 'targetdestroyed'](#event-targetdestroyed)
|
|
* [browser.browserContexts()](#browserbrowsercontexts)
|
|
* [browser.close()](#browserclose)
|
|
* [browser.createIncognitoBrowserContext()](#browsercreateincognitobrowsercontext)
|
|
* [browser.disconnect()](#browserdisconnect)
|
|
* [browser.newPage()](#browsernewpage)
|
|
* [browser.pages()](#browserpages)
|
|
* [browser.process()](#browserprocess)
|
|
* [browser.targets()](#browsertargets)
|
|
* [browser.userAgent()](#browseruseragent)
|
|
* [browser.version()](#browserversion)
|
|
* [browser.wsEndpoint()](#browserwsendpoint)
|
|
- [class: BrowserContext](#class-browsercontext)
|
|
* [event: 'targetchanged'](#event-targetchanged-1)
|
|
* [event: 'targetcreated'](#event-targetcreated-1)
|
|
* [event: 'targetdestroyed'](#event-targetdestroyed-1)
|
|
* [browserContext.browser()](#browsercontextbrowser)
|
|
* [browserContext.close()](#browsercontextclose)
|
|
* [browserContext.isIncognito()](#browsercontextisincognito)
|
|
* [browserContext.newPage()](#browsercontextnewpage)
|
|
* [browserContext.targets()](#browsercontexttargets)
|
|
- [class: Page](#class-page)
|
|
* [event: 'close'](#event-close)
|
|
* [event: 'console'](#event-console)
|
|
* [event: 'dialog'](#event-dialog)
|
|
* [event: 'domcontentloaded'](#event-domcontentloaded)
|
|
* [event: 'error'](#event-error)
|
|
* [event: 'frameattached'](#event-frameattached)
|
|
* [event: 'framedetached'](#event-framedetached)
|
|
* [event: 'framenavigated'](#event-framenavigated)
|
|
* [event: 'load'](#event-load)
|
|
* [event: 'metrics'](#event-metrics)
|
|
* [event: 'pageerror'](#event-pageerror)
|
|
* [event: 'request'](#event-request)
|
|
* [event: 'requestfailed'](#event-requestfailed)
|
|
* [event: 'requestfinished'](#event-requestfinished)
|
|
* [event: 'response'](#event-response)
|
|
* [event: 'workercreated'](#event-workercreated)
|
|
* [event: 'workerdestroyed'](#event-workerdestroyed)
|
|
* [page.$(selector)](#pageselector)
|
|
* [page.$$(selector)](#pageselector-1)
|
|
* [page.$$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])](#pageevalselector-pagefunction-args)
|
|
* [page.$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])](#pageevalselector-pagefunction-args-1)
|
|
* [page.$x(expression)](#pagexexpression)
|
|
* [page.addScriptTag(options)](#pageaddscripttagoptions)
|
|
* [page.addStyleTag(options)](#pageaddstyletagoptions)
|
|
* [page.authenticate(credentials)](#pageauthenticatecredentials)
|
|
* [page.bringToFront()](#pagebringtofront)
|
|
* [page.browser()](#pagebrowser)
|
|
* [page.click(selector[, options])](#pageclickselector-options)
|
|
* [page.close(options)](#pagecloseoptions)
|
|
* [page.content()](#pagecontent)
|
|
* [page.cookies(...urls)](#pagecookiesurls)
|
|
* [page.coverage](#pagecoverage)
|
|
* [page.deleteCookie(...cookies)](#pagedeletecookiecookies)
|
|
* [page.emulate(options)](#pageemulateoptions)
|
|
* [page.emulateMedia(mediaType)](#pageemulatemediamediatype)
|
|
* [page.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)](#pageevaluatepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [page.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)](#pageevaluatehandlepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [page.evaluateOnNewDocument(pageFunction, ...args)](#pageevaluateonnewdocumentpagefunction-args)
|
|
* [page.exposeFunction(name, puppeteerFunction)](#pageexposefunctionname-puppeteerfunction)
|
|
* [page.focus(selector)](#pagefocusselector)
|
|
* [page.frames()](#pageframes)
|
|
* [page.goBack(options)](#pagegobackoptions)
|
|
* [page.goForward(options)](#pagegoforwardoptions)
|
|
* [page.goto(url, options)](#pagegotourl-options)
|
|
* [page.hover(selector)](#pagehoverselector)
|
|
* [page.isClosed()](#pageisclosed)
|
|
* [page.keyboard](#pagekeyboard)
|
|
* [page.mainFrame()](#pagemainframe)
|
|
* [page.metrics()](#pagemetrics)
|
|
* [page.mouse](#pagemouse)
|
|
* [page.pdf(options)](#pagepdfoptions)
|
|
* [page.queryObjects(prototypeHandle)](#pagequeryobjectsprototypehandle)
|
|
* [page.reload(options)](#pagereloadoptions)
|
|
* [page.screenshot([options])](#pagescreenshotoptions)
|
|
* [page.select(selector, ...values)](#pageselectselector-values)
|
|
* [page.setBypassCSP(enabled)](#pagesetbypasscspenabled)
|
|
* [page.setCacheEnabled(enabled)](#pagesetcacheenabledenabled)
|
|
* [page.setContent(html)](#pagesetcontenthtml)
|
|
* [page.setCookie(...cookies)](#pagesetcookiecookies)
|
|
* [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout)
|
|
* [page.setExtraHTTPHeaders(headers)](#pagesetextrahttpheadersheaders)
|
|
* [page.setJavaScriptEnabled(enabled)](#pagesetjavascriptenabledenabled)
|
|
* [page.setOfflineMode(enabled)](#pagesetofflinemodeenabled)
|
|
* [page.setRequestInterception(value)](#pagesetrequestinterceptionvalue)
|
|
* [page.setUserAgent(userAgent)](#pagesetuseragentuseragent)
|
|
* [page.setViewport(viewport)](#pagesetviewportviewport)
|
|
* [page.tap(selector)](#pagetapselector)
|
|
* [page.target()](#pagetarget)
|
|
* [page.title()](#pagetitle)
|
|
* [page.touchscreen](#pagetouchscreen)
|
|
* [page.tracing](#pagetracing)
|
|
* [page.type(selector, text[, options])](#pagetypeselector-text-options)
|
|
* [page.url()](#pageurl)
|
|
* [page.viewport()](#pageviewport)
|
|
* [page.waitFor(selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout[, options[, ...args]])](#pagewaitforselectororfunctionortimeout-options-args)
|
|
* [page.waitForFunction(pageFunction[, options[, ...args]])](#pagewaitforfunctionpagefunction-options-args)
|
|
* [page.waitForNavigation(options)](#pagewaitfornavigationoptions)
|
|
* [page.waitForSelector(selector[, options])](#pagewaitforselectorselector-options)
|
|
* [page.waitForXPath(xpath[, options])](#pagewaitforxpathxpath-options)
|
|
* [page.workers()](#pageworkers)
|
|
- [class: Worker](#class-worker)
|
|
* [worker.executionContext()](#workerexecutioncontext)
|
|
* [worker.url()](#workerurl)
|
|
- [class: Keyboard](#class-keyboard)
|
|
* [keyboard.down(key[, options])](#keyboarddownkey-options)
|
|
* [keyboard.press(key[, options])](#keyboardpresskey-options)
|
|
* [keyboard.sendCharacter(char)](#keyboardsendcharacterchar)
|
|
* [keyboard.type(text, options)](#keyboardtypetext-options)
|
|
* [keyboard.up(key)](#keyboardupkey)
|
|
- [class: Mouse](#class-mouse)
|
|
* [mouse.click(x, y, [options])](#mouseclickx-y-options)
|
|
* [mouse.down([options])](#mousedownoptions)
|
|
* [mouse.move(x, y, [options])](#mousemovex-y-options)
|
|
* [mouse.up([options])](#mouseupoptions)
|
|
- [class: Touchscreen](#class-touchscreen)
|
|
* [touchscreen.tap(x, y)](#touchscreentapx-y)
|
|
- [class: Tracing](#class-tracing)
|
|
* [tracing.start(options)](#tracingstartoptions)
|
|
* [tracing.stop()](#tracingstop)
|
|
- [class: Dialog](#class-dialog)
|
|
* [dialog.accept([promptText])](#dialogacceptprompttext)
|
|
* [dialog.defaultValue()](#dialogdefaultvalue)
|
|
* [dialog.dismiss()](#dialogdismiss)
|
|
* [dialog.message()](#dialogmessage)
|
|
* [dialog.type()](#dialogtype)
|
|
- [class: ConsoleMessage](#class-consolemessage)
|
|
* [consoleMessage.args()](#consolemessageargs)
|
|
* [consoleMessage.text()](#consolemessagetext)
|
|
* [consoleMessage.type()](#consolemessagetype)
|
|
- [class: Frame](#class-frame)
|
|
* [frame.$(selector)](#frameselector)
|
|
* [frame.$$(selector)](#frameselector-1)
|
|
* [frame.$$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])](#frameevalselector-pagefunction-args)
|
|
* [frame.$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])](#frameevalselector-pagefunction-args-1)
|
|
* [frame.$x(expression)](#framexexpression)
|
|
* [frame.addScriptTag(options)](#frameaddscripttagoptions)
|
|
* [frame.addStyleTag(options)](#frameaddstyletagoptions)
|
|
* [frame.childFrames()](#framechildframes)
|
|
* [frame.click(selector[, options])](#frameclickselector-options)
|
|
* [frame.content()](#framecontent)
|
|
* [frame.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)](#frameevaluatepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [frame.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)](#frameevaluatehandlepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [frame.executionContext()](#frameexecutioncontext)
|
|
* [frame.focus(selector)](#framefocusselector)
|
|
* [frame.hover(selector)](#framehoverselector)
|
|
* [frame.isDetached()](#frameisdetached)
|
|
* [frame.name()](#framename)
|
|
* [frame.parentFrame()](#frameparentframe)
|
|
* [frame.select(selector, ...values)](#frameselectselector-values)
|
|
* [frame.setContent(html)](#framesetcontenthtml)
|
|
* [frame.tap(selector)](#frametapselector)
|
|
* [frame.title()](#frametitle)
|
|
* [frame.type(selector, text[, options])](#frametypeselector-text-options)
|
|
* [frame.url()](#frameurl)
|
|
* [frame.waitFor(selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout[, options[, ...args]])](#framewaitforselectororfunctionortimeout-options-args)
|
|
* [frame.waitForFunction(pageFunction[, options[, ...args]])](#framewaitforfunctionpagefunction-options-args)
|
|
* [frame.waitForSelector(selector[, options])](#framewaitforselectorselector-options)
|
|
* [frame.waitForXPath(xpath[, options])](#framewaitforxpathxpath-options)
|
|
- [class: ExecutionContext](#class-executioncontext)
|
|
* [executionContext.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)](#executioncontextevaluatepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [executionContext.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)](#executioncontextevaluatehandlepagefunction-args)
|
|
* [executionContext.frame()](#executioncontextframe)
|
|
* [executionContext.queryObjects(prototypeHandle)](#executioncontextqueryobjectsprototypehandle)
|
|
- [class: JSHandle](#class-jshandle)
|
|
* [jsHandle.asElement()](#jshandleaselement)
|
|
* [jsHandle.dispose()](#jshandledispose)
|
|
* [jsHandle.executionContext()](#jshandleexecutioncontext)
|
|
* [jsHandle.getProperties()](#jshandlegetproperties)
|
|
* [jsHandle.getProperty(propertyName)](#jshandlegetpropertypropertyname)
|
|
* [jsHandle.jsonValue()](#jshandlejsonvalue)
|
|
- [class: ElementHandle](#class-elementhandle)
|
|
* [elementHandle.$(selector)](#elementhandleselector)
|
|
* [elementHandle.$$(selector)](#elementhandleselector-1)
|
|
* [elementHandle.$$eval(selector, pageFunction, ...args)](#elementhandleevalselector-pagefunction-args)
|
|
* [elementHandle.$eval(selector, pageFunction, ...args)](#elementhandleevalselector-pagefunction-args-1)
|
|
* [elementHandle.$x(expression)](#elementhandlexexpression)
|
|
* [elementHandle.asElement()](#elementhandleaselement)
|
|
* [elementHandle.boundingBox()](#elementhandleboundingbox)
|
|
* [elementHandle.boxModel()](#elementhandleboxmodel)
|
|
* [elementHandle.click([options])](#elementhandleclickoptions)
|
|
* [elementHandle.contentFrame()](#elementhandlecontentframe)
|
|
* [elementHandle.dispose()](#elementhandledispose)
|
|
* [elementHandle.executionContext()](#elementhandleexecutioncontext)
|
|
* [elementHandle.focus()](#elementhandlefocus)
|
|
* [elementHandle.getProperties()](#elementhandlegetproperties)
|
|
* [elementHandle.getProperty(propertyName)](#elementhandlegetpropertypropertyname)
|
|
* [elementHandle.hover()](#elementhandlehover)
|
|
* [elementHandle.jsonValue()](#elementhandlejsonvalue)
|
|
* [elementHandle.press(key[, options])](#elementhandlepresskey-options)
|
|
* [elementHandle.screenshot([options])](#elementhandlescreenshotoptions)
|
|
* [elementHandle.tap()](#elementhandletap)
|
|
* [elementHandle.toString()](#elementhandletostring)
|
|
* [elementHandle.type(text[, options])](#elementhandletypetext-options)
|
|
* [elementHandle.uploadFile(...filePaths)](#elementhandleuploadfilefilepaths)
|
|
- [class: Request](#class-request)
|
|
* [request.abort([errorCode])](#requestaborterrorcode)
|
|
* [request.continue([overrides])](#requestcontinueoverrides)
|
|
* [request.failure()](#requestfailure)
|
|
* [request.frame()](#requestframe)
|
|
* [request.headers()](#requestheaders)
|
|
* [request.method()](#requestmethod)
|
|
* [request.postData()](#requestpostdata)
|
|
* [request.redirectChain()](#requestredirectchain)
|
|
* [request.resourceType()](#requestresourcetype)
|
|
* [request.respond(response)](#requestrespondresponse)
|
|
* [request.response()](#requestresponse)
|
|
* [request.url()](#requesturl)
|
|
- [class: Response](#class-response)
|
|
* [response.buffer()](#responsebuffer)
|
|
* [response.fromCache()](#responsefromcache)
|
|
* [response.fromServiceWorker()](#responsefromserviceworker)
|
|
* [response.headers()](#responseheaders)
|
|
* [response.json()](#responsejson)
|
|
* [response.ok()](#responseok)
|
|
* [response.request()](#responserequest)
|
|
* [response.securityDetails()](#responsesecuritydetails)
|
|
* [response.status()](#responsestatus)
|
|
* [response.text()](#responsetext)
|
|
* [response.url()](#responseurl)
|
|
- [class: SecurityDetails](#class-securitydetails)
|
|
* [securityDetails.issuer()](#securitydetailsissuer)
|
|
* [securityDetails.protocol()](#securitydetailsprotocol)
|
|
* [securityDetails.subjectName()](#securitydetailssubjectname)
|
|
* [securityDetails.validFrom()](#securitydetailsvalidfrom)
|
|
* [securityDetails.validTo()](#securitydetailsvalidto)
|
|
- [class: Target](#class-target)
|
|
* [target.browser()](#targetbrowser)
|
|
* [target.browserContext()](#targetbrowsercontext)
|
|
* [target.createCDPSession()](#targetcreatecdpsession)
|
|
* [target.page()](#targetpage)
|
|
* [target.type()](#targettype)
|
|
* [target.url()](#targeturl)
|
|
- [class: CDPSession](#class-cdpsession)
|
|
* [cdpSession.detach()](#cdpsessiondetach)
|
|
* [cdpSession.send(method[, params])](#cdpsessionsendmethod-params)
|
|
- [class: Coverage](#class-coverage)
|
|
* [coverage.startCSSCoverage(options)](#coveragestartcsscoverageoptions)
|
|
* [coverage.startJSCoverage(options)](#coveragestartjscoverageoptions)
|
|
* [coverage.stopCSSCoverage()](#coveragestopcsscoverage)
|
|
* [coverage.stopJSCoverage()](#coveragestopjscoverage)
|
|
<!-- GEN:stop -->
|
|
|
|
### Overview
|
|
|
|
Puppeteer is a Node library which provides a high-level API to control Chromium or Chrome over the DevTools Protocol.
|
|
|
|
The Puppeteer API is hierarchical and mirrors the browser structure.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** On the following diagram, faded entities are not currently represented in Puppeteer.
|
|
|
|
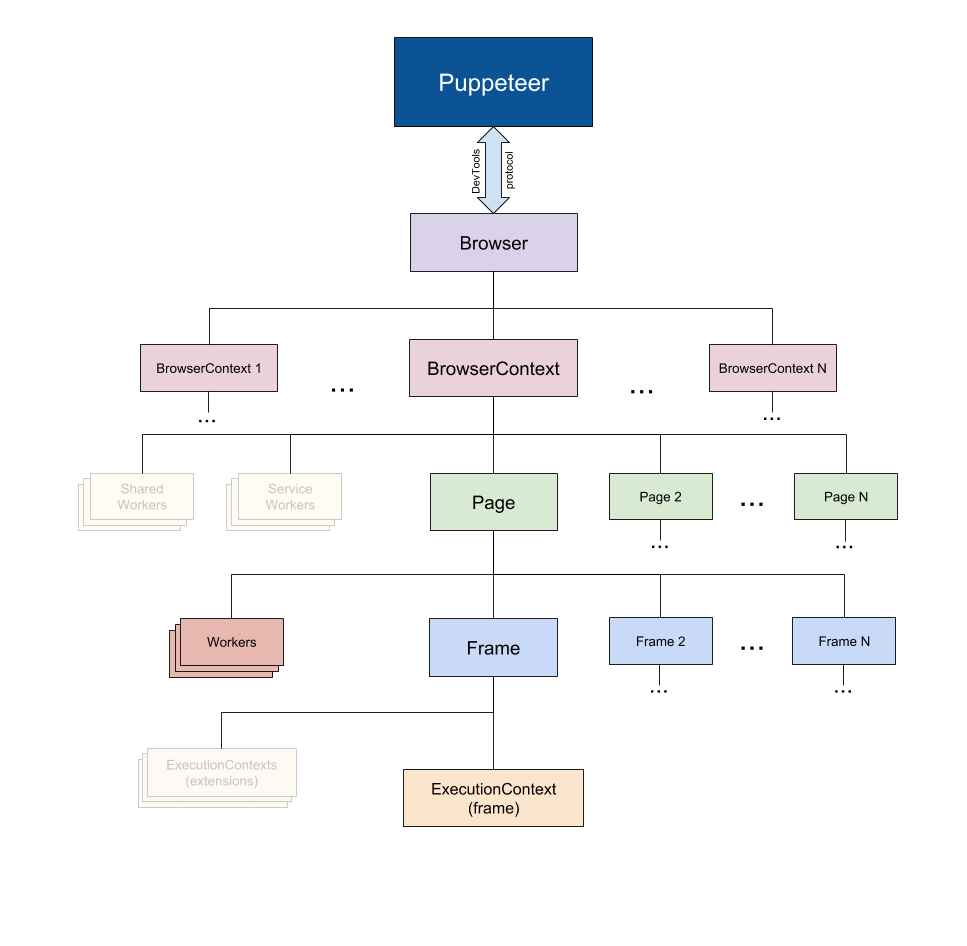
|
|
|
|
- [`Puppeteer`](#class-puppeteer) communicates with the browser using [DevTools Protocol](https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol/).
|
|
- [`Browser`](#class-browser) instance can own multiple browser contexts.
|
|
- [`BrowserContext`](#class-browsercontext) instance defines a browsing session and can own multiple pages.
|
|
- [`Page`](#class-page) has at least one frame: main frame. There might be other frames created by [iframe](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/iframe) or [frame](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/frame) tags.
|
|
- [`Frame`](#class-frame) has at least one execution context - the default execution context - where the frame's JavaScript is executed. A Frame might have additional execution contexts that are associated with [extensions](https://developer.chrome.com/extensions).
|
|
- [`Worker`](#class-worker) has a single execution context and and facilitates interacting with [WebWorkers](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API).
|
|
|
|
(Diagram source: [link](https://docs.google.com/drawings/d/1Q_AM6KYs9kbyLZF-Lpp5mtpAWth73Cq8IKCsWYgi8MM/edit?usp=sharing))
|
|
|
|
### Environment Variables
|
|
|
|
Puppeteer looks for certain [environment variables](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environment_variable) to aid its operations.
|
|
If puppeteer doesn't find them in environment, lowercased variant of these variables will be used from the [npm config](https://docs.npmjs.com/cli/config).
|
|
|
|
- `HTTP_PROXY`, `HTTPS_PROXY`, `NO_PROXY` - defines HTTP proxy settings that are used to download and run Chromium.
|
|
- `PUPPETEER_SKIP_CHROMIUM_DOWNLOAD` - do not download bundled Chromium during installation step.
|
|
- `PUPPETEER_DOWNLOAD_HOST` - overwrite host part of URL that is used to download Chromium
|
|
- `PUPPETEER_CHROMIUM_REVISION` - specify a certain version of chrome you'd like puppeteer to use during the installation step.
|
|
|
|
### class: Puppeteer
|
|
|
|
Puppeteer module provides a method to launch a Chromium instance.
|
|
The following is a typical example of using Puppeteer to drive automation:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.goto('https://www.google.com');
|
|
// other actions...
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### puppeteer.connect(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `browserWSEndpoint` <[string]> a [browser websocket endpoint](#browserwsendpoint) to connect to.
|
|
- `ignoreHTTPSErrors` <[boolean]> Whether to ignore HTTPS errors during navigation. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `slowMo` <[number]> Slows down Puppeteer operations by the specified amount of milliseconds. Useful so that you can see what is going on.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Browser]>>
|
|
|
|
This methods attaches Puppeteer to an existing Chromium instance.
|
|
|
|
#### puppeteer.createBrowserFetcher([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `host` <[string]> A download host to be used. Defaults to `https://storage.googleapis.com`.
|
|
- `path` <[string]> A path for the downloads folder. Defaults to `<root>/.local-chromium`, where `<root>` is puppeteer's package root.
|
|
- `platform` <[string]> Possible values are: `mac`, `win32`, `win64`, `linux`. Defaults to the current platform.
|
|
- returns: <[BrowserFetcher]>
|
|
|
|
#### puppeteer.defaultArgs()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[string]>> The default flags that Chromium will be launched with.
|
|
|
|
#### puppeteer.executablePath()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> A path where Puppeteer expects to find bundled Chromium. Chromium might not exist there if the download was skipped with [`PUPPETEER_SKIP_CHROMIUM_DOWNLOAD`](#environment-variables).
|
|
|
|
#### puppeteer.launch([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Set of configurable options to set on the browser. Can have the following fields:
|
|
- `ignoreHTTPSErrors` <[boolean]> Whether to ignore HTTPS errors during navigation. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `headless` <[boolean]> Whether to run browser in [headless mode](https://developers.google.com/web/updates/2017/04/headless-chrome). Defaults to `true` unless the `devtools` option is `true`.
|
|
- `executablePath` <[string]> Path to a Chromium or Chrome executable to run instead of the bundled Chromium. If `executablePath` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- `slowMo` <[number]> Slows down Puppeteer operations by the specified amount of milliseconds. Useful so that you can see what is going on.
|
|
- `args` <[Array]<[string]>> Additional arguments to pass to the browser instance. The list of Chromium flags can be found [here](http://peter.sh/experiments/chromium-command-line-switches/).
|
|
- `ignoreDefaultArgs` <[boolean]> Do not use [`puppeteer.defaultArgs()`](#puppeteerdefaultargs). Dangerous option; use with care. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `handleSIGINT` <[boolean]> Close the browser process on Ctrl-C. Defaults to `true`.
|
|
- `handleSIGTERM` <[boolean]> Close the browser process on SIGTERM. Defaults to `true`.
|
|
- `handleSIGHUP` <[boolean]> Close the browser process on SIGHUP. Defaults to `true`.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum time in milliseconds to wait for the browser instance to start. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- `dumpio` <[boolean]> Whether to pipe the browser process stdout and stderr into `process.stdout` and `process.stderr`. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `userDataDir` <[string]> Path to a [User Data Directory](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/src/+/master/docs/user_data_dir.md).
|
|
- `env` <[Object]> Specify environment variables that will be visible to the browser. Defaults to `process.env`.
|
|
- `devtools` <[boolean]> Whether to auto-open a DevTools panel for each tab. If this option is `true`, the `headless` option will be set `false`.
|
|
- `pipe` <[boolean]> Connects to the browser over a pipe instead of a WebSocket. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Browser]>> Promise which resolves to browser instance.
|
|
|
|
The method launches a browser instance with given arguments. The browser will be closed when the parent node.js process is closed.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Puppeteer can also be used to control the Chrome browser, but it works best with the version of Chromium it is bundled with. There is no guarantee it will work with any other version. Use `executablePath` option with extreme caution.
|
|
>
|
|
> If Google Chrome (rather than Chromium) is preferred, a [Chrome Canary](https://www.google.com/chrome/browser/canary.html) or [Dev Channel](https://www.chromium.org/getting-involved/dev-channel) build is suggested.
|
|
>
|
|
> In [puppeteer.launch([options])](#puppeteerlaunchoptions) above, any mention of Chromium also applies to Chrome.
|
|
>
|
|
> See [`this article`](https://www.howtogeek.com/202825/what%E2%80%99s-the-difference-between-chromium-and-chrome/) for a description of the differences between Chromium and Chrome. [`This article`](https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/src/+/lkcr/docs/chromium_browser_vs_google_chrome.md) describes some differences for Linux users.
|
|
|
|
### class: BrowserFetcher
|
|
|
|
BrowserFetcher can download and manage different versions of Chromium.
|
|
|
|
BrowserFetcher operates on revision strings that specify a precise version of Chromium, e.g. `"533271"`. Revision strings can be obtained from [omahaproxy.appspot.com](http://omahaproxy.appspot.com/).
|
|
|
|
Example on how to use BrowserFetcher to download a specific version of Chromium and run
|
|
Puppeteer against it:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const browserFetcher = puppeteer.createBrowserFetcher();
|
|
const revisionInfo = await browserFetcher.download('533271');
|
|
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({executablePath: revisionInfo.executablePath})
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** BrowserFetcher is not designed to work concurrently with other
|
|
> instances of BrowserFetcher that share the same downloads directory.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.canDownload(revision)
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> a revision to check availability.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[boolean]>> returns `true` if the revision could be downloaded from the host.
|
|
|
|
The method initiates a HEAD request to check if the revision is available.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.download(revision[, progressCallback])
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> a revision to download.
|
|
- `progressCallback` <[function]([number], [number])> A function that will be called with two arguments:
|
|
- `downloadedBytes` <[number]> how many bytes have been downloaded
|
|
- `totalBytes` <[number]> how large is the total download.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Object]>> Resolves with revision information when the revision is downloaded and extracted
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> the revision the info was created from
|
|
- `folderPath` <[string]> path to the extracted revision folder
|
|
- `executablePath` <[string]> path to the revision executable
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL this revision can be downloaded from
|
|
- `local` <[boolean]> whether the revision is locally available on disk
|
|
|
|
The method initiates a GET request to download the revision from the host.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.localRevisions()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[string]>>> A list of all revisions available locally on disk.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.platform()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Returns one of `mac`, `linux`, `win32` or `win64`.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.remove(revision)
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> a revision to remove. The method will throw if the revision has not been downloaded.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Resolves when the revision has been removed.
|
|
|
|
#### browserFetcher.revisionInfo(revision)
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> a revision to get info for.
|
|
- returns: <[Object]>
|
|
- `revision` <[string]> the revision the info was created from
|
|
- `folderPath` <[string]> path to the extracted revision folder
|
|
- `executablePath` <[string]> path to the revision executable
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL this revision can be downloaded from
|
|
- `local` <[boolean]> whether the revision is locally available on disk
|
|
|
|
### class: Browser
|
|
|
|
* extends: [`EventEmitter`](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_class_eventemitter)
|
|
|
|
A Browser is created when Puppeteer connects to a Chromium instance, either through [`puppeteer.launch`](#puppeteerlaunchoptions) or [`puppeteer.connect`](#puppeteerconnectoptions).
|
|
|
|
An example of using a [Browser] to create a [Page]:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
An example of disconnecting from and reconnecting to a [Browser]:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
// Store the endpoint to be able to reconnect to Chromium
|
|
const browserWSEndpoint = browser.wsEndpoint();
|
|
// Disconnect puppeteer from Chromium
|
|
browser.disconnect();
|
|
|
|
// Use the endpoint to reestablish a connection
|
|
const browser2 = await puppeteer.connect({browserWSEndpoint});
|
|
// Close Chromium
|
|
await browser2.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
#### event: 'disconnected'
|
|
Emitted when Puppeteer gets disconnected from the Chromium instance. This might happen because of one of the following:
|
|
- Chromium is closed or crashed
|
|
- The [`browser.disconnect`](#browserdisconnect) method was called
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetchanged'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the url of a target changes.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** This includes target changes in incognito browser contexts.
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetcreated'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a target is created, for example when a new page is opened by [`window.open`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/open) or [`browser.newPage`](#browsernewpage).
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** This includes target creations in incognito browser contexts.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetdestroyed'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a target is destroyed, for example when a page is closed.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** This includes target destructions in incognito browser contexts.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.browserContexts()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[BrowserContext]>>
|
|
|
|
Returns an array of all open browser contexts. In a newly created browser, this will return
|
|
a single instance of [BrowserContext].
|
|
|
|
#### browser.close()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Closes Chromium and all of its pages (if any were opened). The [Browser] object itself is considered to be disposed and cannot be used anymore.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.createIncognitoBrowserContext()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[BrowserContext]>>
|
|
|
|
Creates a new incognito browser context. This won't share cookies/cache with other browser contexts.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
|
|
// Create a new incognito browser context.
|
|
const context = await browser.createIncognitoBrowserContext();
|
|
// Create a new page in a pristine context.
|
|
const page = await context.newPage();
|
|
// Do stuff
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### browser.disconnect()
|
|
|
|
Disconnects Puppeteer from the browser, but leaves the Chromium process running. After calling `disconnect`, the [Browser] object is considered disposed and cannot be used anymore.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.newPage()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Page]>>
|
|
|
|
Promise which resolves to a new [Page] object. The [Page] is created in a default browser context.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.pages()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[Page]>>> Promise which resolves to an array of all open pages.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.process()
|
|
- returns: <?[ChildProcess]> Spawned browser process. Returns `null` if the browser instance was created with [`puppeteer.connect`](#puppeteerconnectoptions) method.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.targets()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Target]>>
|
|
|
|
An array of all active targets inside the Browser. In case of multiple browser contexts,
|
|
the method will return an array with all the targets in all browser contexts.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.userAgent()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[string]>> Promise which resolves to the browser's original user agent.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Pages can override browser user agent with [page.setUserAgent](#pagesetuseragentuseragent)
|
|
|
|
#### browser.version()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[string]>> For headless Chromium, this is similar to `HeadlessChrome/61.0.3153.0`. For non-headless, this is similar to `Chrome/61.0.3153.0`.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** the format of browser.version() might change with future releases of Chromium.
|
|
|
|
#### browser.wsEndpoint()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Browser websocket url.
|
|
|
|
Browser websocket endpoint which can be used as an argument to
|
|
[puppeteer.connect](#puppeteerconnectoptions). The format is `ws://${host}:${port}/devtools/browser/<id>`
|
|
|
|
You can find the `webSocketDebuggerUrl` from `http://${host}:${port}/json/version`. Learn more about the [devtools protocol](https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol) and the [browser endpoint](https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol/#how-do-i-access-the-browser-target).
|
|
|
|
### class: BrowserContext
|
|
|
|
* extends: [`EventEmitter`](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_class_eventemitter)
|
|
|
|
BrowserContexts provide a way to operate multiple independent browser sessions. When a browser is launched, it has
|
|
a single BrowserContext used by default. The method `browser.newPage()` creates a page in the default browser context.
|
|
|
|
If a page opens another page, e.g. with a `window.open` call, the popup will belong to the parent page's browser
|
|
context.
|
|
|
|
Puppeteer allows creation of "incognito" browser contexts with `browser.createIncognitoBrowserContext()` method.
|
|
"Incognito" browser contexts don't write any browsing data to disk.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Create a new incognito browser context
|
|
const context = await browser.createIncognitoBrowserContext();
|
|
// Create a new page inside context.
|
|
const page = await context.newPage();
|
|
// ... do stuff with page ...
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
// Dispose context once it's no longer needed.
|
|
await context.close();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetchanged'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the url of a target inside the browser context changes.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetcreated'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a new target is created inside the browser context, for example when a new page is opened by [`window.open`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/open) or [`browserContext.newPage`](#browsercontextnewpage).
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'targetdestroyed'
|
|
- <[Target]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a target inside the browser context is destroyed, for example when a page is closed.
|
|
|
|
#### browserContext.browser()
|
|
- returns: <[Browser]>
|
|
|
|
The browser this browser context belongs to.
|
|
|
|
#### browserContext.close()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Closes the browser context. All the targets that belong to the browser context
|
|
will be closed.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** only incognito browser contexts can be closed.
|
|
|
|
#### browserContext.isIncognito()
|
|
- returns: <[boolean]>
|
|
|
|
Returns whether BrowserContext is incognito.
|
|
The default browser context is the only non-incognito browser context.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** the default browser context cannot be closed.
|
|
|
|
#### browserContext.newPage()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Page]>>
|
|
|
|
Creates a new page in the browser context.
|
|
|
|
#### browserContext.targets()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Target]>>
|
|
|
|
An array of all active targets inside the browser context.
|
|
|
|
### class: Page
|
|
|
|
* extends: [`EventEmitter`](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_class_eventemitter)
|
|
|
|
Page provides methods to interact with a single tab in Chromium. One [Browser] instance might have multiple [Page] instances.
|
|
|
|
This example creates a page, navigates it to a URL, and then saves a screenshot:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
await page.screenshot({path: 'screenshot.png'});
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The Page class emits various events (described below) which can be handled using any of Node's native [`EventEmitter`](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_class_eventemitter) methods, such as `on`, `once` or `removeListener`.
|
|
|
|
This example logs a message for a single page `load` event:
|
|
```js
|
|
page.once('load', () => console.log('Page loaded!'));
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
To unsubscribe from events use the `removeListener` method:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
function logRequest(interceptedRequest) {
|
|
console.log('A request was made:', interceptedRequest.url());
|
|
}
|
|
page.on('request', logRequest);
|
|
// Sometime later...
|
|
page.removeListener('request', logRequest);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'close'
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the page closes.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'console'
|
|
- <[ConsoleMessage]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when JavaScript within the page calls one of console API methods, e.g. `console.log` or `console.dir`. Also emitted if the page throws an error or a warning.
|
|
|
|
The arguments passed into `console.log` appear as arguments on the event handler.
|
|
|
|
An example of handling `console` event:
|
|
```js
|
|
page.on('console', msg => {
|
|
for (let i = 0; i < msg.args().length; ++i)
|
|
console.log(`${i}: ${msg.args()[i]}`);
|
|
});
|
|
page.evaluate(() => console.log('hello', 5, {foo: 'bar'}));
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'dialog'
|
|
- <[Dialog]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a JavaScript dialog appears, such as `alert`, `prompt`, `confirm` or `beforeunload`. Puppeteer can respond to the dialog via [Dialog]'s [accept](#dialogacceptprompttext) or [dismiss](#dialogdismiss) methods.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'domcontentloaded'
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the JavaScript [`DOMContentLoaded`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Events/DOMContentLoaded) event is dispatched.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'error'
|
|
- <[Error]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the page crashes.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** `error` event has a special meaning in Node, see [error events](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_error_events) for details.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'frameattached'
|
|
- <[Frame]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a frame is attached.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'framedetached'
|
|
- <[Frame]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a frame is detached.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'framenavigated'
|
|
- <[Frame]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a frame is navigated to a new url.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'load'
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the JavaScript [`load`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Events/load) event is dispatched.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'metrics'
|
|
- <[Object]>
|
|
- `title` <[string]> The title passed to `console.timeStamp`.
|
|
- `metrics` <[Object]> Object containing metrics as key/value pairs. The values
|
|
of metrics are of <[number]> type.
|
|
|
|
Emitted when the JavaScript code makes a call to `console.timeStamp`. For the list
|
|
of metrics see `page.metrics`.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'pageerror'
|
|
- <[Error]> The exception message
|
|
|
|
Emitted when an uncaught exception happens within the page.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'request'
|
|
- <[Request]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a page issues a request. The [request] object is read-only.
|
|
In order to intercept and mutate requests, see `page.setRequestInterception`.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'requestfailed'
|
|
- <[Request]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a request fails, for example by timing out.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'requestfinished'
|
|
- <[Request]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a request finishes successfully.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'response'
|
|
- <[Response]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a [response] is received.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'workercreated'
|
|
- <[Worker]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a dedicated [WebWorker](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API) is spawned by the page.
|
|
|
|
#### event: 'workerdestroyed'
|
|
- <[Worker]>
|
|
|
|
Emitted when a dedicated [WebWorker](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API) is terminated.
|
|
|
|
#### page.$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[ElementHandle]>>
|
|
|
|
The method runs `document.querySelector` within the page. If no element matches the selector, the return value resolve to `null`.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().$(selector)](#frameselector).
|
|
|
|
#### page.$$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[ElementHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method runs `document.querySelectorAll` within the page. If no elements match the selector, the return value resolve to `[]`.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().$$(selector)](#frameselector-1).
|
|
|
|
#### page.$$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query frame for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `Array.from(document.querySelectorAll(selector))` within the page and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `page.$$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```js
|
|
const divsCounts = await page.$$eval('div', divs => divs.length);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### page.$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `document.querySelector` within the page and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`. If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `page.$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```js
|
|
const searchValue = await page.$eval('#search', el => el.value);
|
|
const preloadHref = await page.$eval('link[rel=preload]', el => el.href);
|
|
const html = await page.$eval('.main-container', e => e.outerHTML);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().$eval(selector, pageFunction)](#frameevalselector-pagefunction-args).
|
|
|
|
#### page.$x(expression)
|
|
- `expression` <[string]> Expression to [evaluate](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Document/evaluate).
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[ElementHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method evaluates the XPath expression.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().$x(expression)](#framexexpression)
|
|
|
|
#### page.addScriptTag(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL of a script to be added.
|
|
- `path` <[string]> Path to the JavaScript file to be injected into frame. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- `content` <[string]> Raw JavaScript content to be injected into frame.
|
|
- `type` <[string]> Script type. Use 'module' in order to load a Javascript ES6 module. See [script](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/script) for more details.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> which resolves to the added tag when the script's onload fires or when the script content was injected into frame.
|
|
|
|
Adds a `<script>` tag into the page with the desired url or content.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().addScriptTag(options)](#frameaddscripttagoptions).
|
|
|
|
#### page.addStyleTag(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL of the `<link>` tag.
|
|
- `path` <[string]> Path to the CSS file to be injected into frame. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- `content` <[string]> Raw CSS content to be injected into frame.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> which resolves to the added tag when the stylesheet's onload fires or when the CSS content was injected into frame.
|
|
|
|
Adds a `<link rel="stylesheet">` tag into the page with the desired url or a `<style type="text/css">` tag with the content.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().addStyleTag(options)](#frameaddstyletagoptions).
|
|
|
|
#### page.authenticate(credentials)
|
|
- `credentials` <?[Object]>
|
|
- `username` <[string]>
|
|
- `password` <[string]>
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Provide credentials for [http authentication](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication).
|
|
|
|
To disable authentication, pass `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### page.bringToFront()
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Brings page to front (activates tab).
|
|
|
|
#### page.browser()
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Browser]>
|
|
|
|
Get the browser the page belongs to.
|
|
|
|
#### page.click(selector[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to click. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be clicked.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `mousedown` and `mouseup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully clicked. The Promise will be rejected if there is no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to click in the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
Bear in mind that if `click()` triggers a navigation event and there's a separate `page.waitForNavigation()` promise to be resolved, you may end up with a race condition that yields unexpected results. The correct pattern for click and wait for navigation is the following:
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
const [response] = await Promise.all([
|
|
page.waitForNavigation(waitOptions),
|
|
page.click(selector, clickOptions),
|
|
]);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().click(selector[, options])](#frameclickselector-options).
|
|
|
|
#### page.close(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `runBeforeUnload` <[boolean]> Defaults to `false`. Whether to run the
|
|
[before unload](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Events/beforeunload)
|
|
page handlers.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
By default, `page.close()` **does not** run beforeunload handlers.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** if `runBeforeUnload` is passed as true, a `beforeunload` dialog might be summoned
|
|
> and should be handled manually via page's ['dialog'](#event-dialog) event.
|
|
|
|
#### page.content()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[String]>>
|
|
|
|
Gets the full HTML contents of the page, including the doctype.
|
|
|
|
#### page.cookies(...urls)
|
|
- `...urls` <...[string]>
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[Object]>>>
|
|
- `name` <[string]>
|
|
- `value` <[string]>
|
|
- `domain` <[string]>
|
|
- `path` <[string]>
|
|
- `expires` <[number]> Unix time in seconds.
|
|
- `httpOnly` <[boolean]>
|
|
- `secure` <[boolean]>
|
|
- `session` <[boolean]>
|
|
- `sameSite` <[string]> `"Strict"` or `"Lax"`.
|
|
|
|
If no URLs are specified, this method returns cookies for the current page URL.
|
|
If URLs are specified, only cookies for those URLs are returned.
|
|
|
|
#### page.coverage
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Coverage]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.deleteCookie(...cookies)
|
|
- `...cookies` <...[Object]>
|
|
- `name` <[string]> **required**
|
|
- `url` <[string]>
|
|
- `domain` <[string]>
|
|
- `path` <[string]>
|
|
- `secure` <[boolean]>
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.emulate(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `viewport` <[Object]>
|
|
- `width` <[number]> page width in pixels.
|
|
- `height` <[number]> page height in pixels.
|
|
- `deviceScaleFactor` <[number]> Specify device scale factor (can be thought of as dpr). Defaults to `1`.
|
|
- `isMobile` <[boolean]> Whether the `meta viewport` tag is taken into account. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hasTouch`<[boolean]> Specifies if viewport supports touch events. Defaults to `false`
|
|
- `isLandscape` <[boolean]> Specifies if viewport is in landscape mode. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `userAgent` <[string]>
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Emulates given device metrics and user agent. This method is a shortcut for calling two methods:
|
|
- [page.setUserAgent(userAgent)](#pagesetuseragentuseragent)
|
|
- [page.setViewport(viewport)](#pagesetviewportviewport)
|
|
|
|
To aid emulation, puppeteer provides a list of device descriptors which can be obtained via the `require('puppeteer/DeviceDescriptors')` command.
|
|
Below is an example of emulating an iPhone 6 in puppeteer:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
const devices = require('puppeteer/DeviceDescriptors');
|
|
const iPhone = devices['iPhone 6'];
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.emulate(iPhone);
|
|
await page.goto('https://www.google.com');
|
|
// other actions...
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
List of all available devices is available in the source code: [DeviceDescriptors.js](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/blob/master/DeviceDescriptors.js).
|
|
|
|
#### page.emulateMedia(mediaType)
|
|
- `mediaType` <?[string]> Changes the CSS media type of the page. The only allowed values are `'screen'`, `'print'` and `null`. Passing `null` disables media emulation.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in the page context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `page.evaluate` returns a [Promise], then `page.evaluate` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `page.evaluate` returns a non-[Serializable] value, then `page.evaluate` resolves to `undefined`.
|
|
|
|
Passing arguments to `pageFunction`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const result = await page.evaluate(x => {
|
|
return Promise.resolve(8 * x);
|
|
}, 7);
|
|
console.log(result); // prints "56"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function:
|
|
```js
|
|
console.log(await page.evaluate('1 + 2')); // prints "3"
|
|
const x = 10;
|
|
console.log(await page.evaluate(`1 + ${x}`)); // prints "11"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[ElementHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `page.evaluate`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const bodyHandle = await page.$('body');
|
|
const html = await page.evaluate(body => body.innerHTML, bodyHandle);
|
|
await bodyHandle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)](#frameevaluatepagefunction-args).
|
|
|
|
#### page.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in the page context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction` as in-page object (JSHandle)
|
|
|
|
The only difference between `page.evaluate` and `page.evaluateHandle` is that `page.evaluateHandle` returns in-page object (JSHandle).
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `page.evaluateHandle` returns a [Promise], then `page.evaluateHandle` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function:
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await page.evaluateHandle('document'); // Handle for the 'document'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[JSHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `page.evaluateHandle`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await page.evaluateHandle(() => document.body);
|
|
const resultHandle = await page.evaluateHandle(body => body.innerHTML, aHandle);
|
|
console.log(await resultHandle.jsonValue());
|
|
await resultHandle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().executionContext().evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)](#executioncontextevaluatehandlepagefunction-args).
|
|
|
|
#### page.evaluateOnNewDocument(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Adds a function which would be invoked in one of the following scenarios:
|
|
- whenever the page is navigated
|
|
- whenever the child frame is attached or navigated. In this case, the function is invoked in the context of the newly attached frame
|
|
|
|
The function is invoked after the document was created but before any of its scripts were run. This is useful to amend the JavaScript environment, e.g. to seed `Math.random`.
|
|
|
|
An example of overriding the navigator.languages property before the page loads:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// preload.js
|
|
|
|
// overwrite the `languages` property to use a custom getter
|
|
Object.defineProperty(navigator, "languages", {
|
|
get: function() {
|
|
return ["en-US", "en", "bn"];
|
|
}
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
// In your puppeteer script, assuming the preload.js file is in same folder of our script
|
|
const preloadFile = fs.readFileSync('./preload.js', 'utf8');
|
|
await page.evaluateOnNewDocument(preloadFile);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### page.exposeFunction(name, puppeteerFunction)
|
|
- `name` <[string]> Name of the function on the window object
|
|
- `puppeteerFunction` <[function]> Callback function which will be called in Puppeteer's context.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
The method adds a function called `name` on the page's `window` object.
|
|
When called, the function executes `puppeteerFunction` in node.js and returns a [Promise] which resolves to the return value of `puppeteerFunction`.
|
|
|
|
If the `puppeteerFunction` returns a [Promise], it will be awaited.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Functions installed via `page.exposeFunction` survive navigations.
|
|
|
|
An example of adding an `md5` function into the page:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
const crypto = require('crypto');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
page.on('console', msg => console.log(msg.text()));
|
|
await page.exposeFunction('md5', text =>
|
|
crypto.createHash('md5').update(text).digest('hex')
|
|
);
|
|
await page.evaluate(async () => {
|
|
// use window.md5 to compute hashes
|
|
const myString = 'PUPPETEER';
|
|
const myHash = await window.md5(myString);
|
|
console.log(`md5 of ${myString} is ${myHash}`);
|
|
});
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
An example of adding a `window.readfile` function into the page:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
const fs = require('fs');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
page.on('console', msg => console.log(msg.text()));
|
|
await page.exposeFunction('readfile', async filePath => {
|
|
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
|
|
fs.readFile(filePath, 'utf8', (err, text) => {
|
|
if (err)
|
|
reject(err);
|
|
else
|
|
resolve(text);
|
|
});
|
|
});
|
|
});
|
|
await page.evaluate(async () => {
|
|
// use window.readfile to read contents of a file
|
|
const content = await window.readfile('/etc/hosts');
|
|
console.log(content);
|
|
});
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### page.focus(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to focus. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be focused.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully focused. The promise will be rejected if there is no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector` and focuses it.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().focus(selector)](#framefocusselector).
|
|
|
|
#### page.frames()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Frame]>> An array of all frames attached to the page.
|
|
|
|
#### page.goBack(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Navigation parameters which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds, defaults to 30 seconds, pass `0` to disable timeout. The default value can be changed by using the [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout) method.
|
|
- `waitUntil` <[string]|[Array]<[string]>> When to consider navigation succeeded, defaults to `load`. Given an array of event strings, navigation is considered to be successful after all events have been fired. Events can be either:
|
|
- `load` - consider navigation to be finished when the `load` event is fired.
|
|
- `domcontentloaded` - consider navigation to be finished when the `DOMContentLoaded` event is fired.
|
|
- `networkidle0` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 0 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- `networkidle2` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 2 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Response]>> Promise which resolves to the main resource response. In case of multiple redirects, the navigation will resolve with the response of the last redirect. If
|
|
can not go back, resolves to `null`.
|
|
|
|
Navigate to the previous page in history.
|
|
|
|
#### page.goForward(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Navigation parameters which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds, defaults to 30 seconds, pass `0` to disable timeout. The default value can be changed by using the [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout) method.
|
|
- `waitUntil` <[string]|[Array]<[string]>> When to consider navigation succeeded, defaults to `load`. Given an array of event strings, navigation is considered to be successful after all events have been fired. Events can be either:
|
|
- `load` - consider navigation to be finished when the `load` event is fired.
|
|
- `domcontentloaded` - consider navigation to be finished when the `DOMContentLoaded` event is fired.
|
|
- `networkidle0` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 0 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- `networkidle2` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 2 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Response]>> Promise which resolves to the main resource response. In case of multiple redirects, the navigation will resolve with the response of the last redirect. If
|
|
can not go forward, resolves to `null`.
|
|
|
|
Navigate to the next page in history.
|
|
|
|
#### page.goto(url, options)
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL to navigate page to. The url should include scheme, e.g. `https://`.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Navigation parameters which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds, defaults to 30 seconds, pass `0` to disable timeout. The default value can be changed by using the [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout) method.
|
|
- `waitUntil` <[string]|[Array]<[string]>> When to consider navigation succeeded, defaults to `load`. Given an array of event strings, navigation is considered to be successful after all events have been fired. Events can be either:
|
|
- `load` - consider navigation to be finished when the `load` event is fired.
|
|
- `domcontentloaded` - consider navigation to be finished when the `DOMContentLoaded` event is fired.
|
|
- `networkidle0` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 0 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- `networkidle2` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 2 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Response]>> Promise which resolves to the main resource response. In case of multiple redirects, the navigation will resolve with the response of the last redirect.
|
|
|
|
The `page.goto` will throw an error if:
|
|
- there's an SSL error (e.g. in case of self-signed certificates).
|
|
- target URL is invalid.
|
|
- the `timeout` is exceeded during navigation.
|
|
- the main resource failed to load.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** `page.goto` either throw or return a main resource response. The only exception is navigation to `about:blank`, which would succeed and return `null`.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Headless mode doesn't support navigating to a PDF document. See the [upstream issue](https://bugs.chromium.org/p/chromium/issues/detail?id=761295).
|
|
|
|
#### page.hover(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to hover. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be hovered.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully hovered. Promise gets rejected if there's no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to hover over the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().hover(selector)](#framehoverselector).
|
|
|
|
#### page.isClosed()
|
|
|
|
- returns: boolean
|
|
|
|
Indicates that the page has been closed.
|
|
|
|
#### page.keyboard
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Keyboard]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.mainFrame()
|
|
- returns: <[Frame]> returns page's main frame.
|
|
|
|
Page is guaranteed to have a main frame which persists during navigations.
|
|
|
|
#### page.metrics()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Object]>> Object containing metrics as key/value pairs.
|
|
- `Timestamp` <[number]> The timestamp when the metrics sample was taken.
|
|
- `Documents` <[number]> Number of documents in the page.
|
|
- `Frames` <[number]> Number of frames in the page.
|
|
- `JSEventListeners` <[number]> Number of events in the page.
|
|
- `Nodes` <[number]> Number of DOM nodes in the page.
|
|
- `LayoutCount` <[number]> Total number of full or partial page layout.
|
|
- `RecalcStyleCount` <[number]> Total number of page style recalculations.
|
|
- `LayoutDuration` <[number]> Combined durations of all page layouts.
|
|
- `RecalcStyleDuration` <[number]> Combined duration of all page style recalculations.
|
|
- `ScriptDuration` <[number]> Combined duration of JavaScript execution.
|
|
- `TaskDuration` <[number]> Combined duration of all tasks performed by the browser.
|
|
- `JSHeapUsedSize` <[number]> Used JavaScript heap size.
|
|
- `JSHeapTotalSize` <[number]> Total JavaScript heap size.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** All timestamps are in monotonic time: monotonically increasing time in seconds since an arbitrary point in the past.
|
|
|
|
#### page.mouse
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Mouse]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.pdf(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Options object which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `path` <[string]> The file path to save the PDF to. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd). If no path is provided, the PDF won't be saved to the disk.
|
|
- `scale` <[number]> Scale of the webpage rendering. Defaults to `1`.
|
|
- `displayHeaderFooter` <[boolean]> Display header and footer. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `headerTemplate` <[string]> HTML template for the print header. Should be valid HTML markup with following classes used to inject printing values into them:
|
|
- `date` formatted print date
|
|
- `title` document title
|
|
- `url` document location
|
|
- `pageNumber` current page number
|
|
- `totalPages` total pages in the document
|
|
- `footerTemplate` <[string]> HTML template for the print footer. Should use the same format as the `headerTemplate`.
|
|
- `printBackground` <[boolean]> Print background graphics. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `landscape` <[boolean]> Paper orientation. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `pageRanges` <[string]> Paper ranges to print, e.g., '1-5, 8, 11-13'. Defaults to the empty string, which means print all pages.
|
|
- `format` <[string]> Paper format. If set, takes priority over `width` or `height` options. Defaults to 'Letter'.
|
|
- `width` <[string]> Paper width, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- `height` <[string]> Paper height, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- `margin` <[Object]> Paper margins, defaults to none.
|
|
- `top` <[string]> Top margin, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- `right` <[string]> Right margin, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- `bottom` <[string]> Bottom margin, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- `left` <[string]> Left margin, accepts values labeled with units.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Buffer]>> Promise which resolves with PDF buffer.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Generating a pdf is currently only supported in Chrome headless.
|
|
|
|
`page.pdf()` generates a pdf of the page with `print` css media. To generate a pdf with `screen` media, call [page.emulateMedia('screen')](#pageemulatemediamediatype) before calling `page.pdf()`:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Generates a PDF with 'screen' media type.
|
|
await page.emulateMedia('screen');
|
|
await page.pdf({path: 'page.pdf'});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `width`, `height`, and `margin` options accept values labeled with units. Unlabeled values are treated as pixels.
|
|
|
|
A few examples:
|
|
- `page.pdf({width: 100})` - prints with width set to 100 pixels
|
|
- `page.pdf({width: '100px'})` - prints with width set to 100 pixels
|
|
- `page.pdf({width: '10cm'})` - prints with width set to 10 centimeters.
|
|
|
|
All possible units are:
|
|
- `px` - pixel
|
|
- `in` - inch
|
|
- `cm` - centimeter
|
|
- `mm` - millimeter
|
|
|
|
The `format` options are:
|
|
- `Letter`: 8.5in x 11in
|
|
- `Legal`: 8.5in x 14in
|
|
- `Tabloid`: 11in x 17in
|
|
- `Ledger`: 17in x 11in
|
|
- `A0`: 33.1in x 46.8in
|
|
- `A1`: 23.4in x 33.1in
|
|
- `A2`: 16.5in x 23.4in
|
|
- `A3`: 11.7in x 16.5in
|
|
- `A4`: 8.27in x 11.7in
|
|
- `A5`: 5.83in x 8.27in
|
|
- `A6`: 4.13in x 5.83in
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** `headerTemplate` and `footerTemplate` markup have the following limitations:
|
|
> 1. Script tags inside templates are not evaluated.
|
|
> 2. Page styles are not visible inside templates.
|
|
|
|
#### page.queryObjects(prototypeHandle)
|
|
- `prototypeHandle` <[JSHandle]> A handle to the object prototype.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to a handle to an array of objects with this prototype.
|
|
|
|
The method iterates the JavaScript heap and finds all the objects with the given prototype.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Create a Map object
|
|
await page.evaluate(() => window.map = new Map());
|
|
// Get a handle to the Map object prototype
|
|
const mapPrototype = await page.evaluateHandle(() => Map.prototype);
|
|
// Query all map instances into an array
|
|
const mapInstances = await page.queryObjects(mapPrototype);
|
|
// Count amount of map objects in heap
|
|
const count = await page.evaluate(maps => maps.length, mapInstances);
|
|
await mapInstances.dispose();
|
|
await mapPrototype.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().executionContext().queryObjects(prototypeHandle)](#executioncontextqueryobjectsprototypehandle).
|
|
|
|
#### page.reload(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Navigation parameters which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds, defaults to 30 seconds, pass `0` to disable timeout. The default value can be changed by using the [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout) method.
|
|
- `waitUntil` <[string]|[Array]<[string]>> When to consider navigation succeeded, defaults to `load`. Given an array of event strings, navigation is considered to be successful after all events have been fired. Events can be either:
|
|
- `load` - consider navigation to be finished when the `load` event is fired.
|
|
- `domcontentloaded` - consider navigation to be finished when the `DOMContentLoaded` event is fired.
|
|
- `networkidle0` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 0 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- `networkidle2` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 2 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Response]>> Promise which resolves to the main resource response. In case of multiple redirects, the navigation will resolve with the response of the last redirect.
|
|
|
|
#### page.screenshot([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Options object which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `path` <[string]> The file path to save the image to. The screenshot type will be inferred from file extension. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd). If no path is provided, the image won't be saved to the disk.
|
|
- `type` <[string]> Specify screenshot type, can be either `jpeg` or `png`. Defaults to 'png'.
|
|
- `quality` <[number]> The quality of the image, between 0-100. Not applicable to `png` images.
|
|
- `fullPage` <[boolean]> When true, takes a screenshot of the full scrollable page. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `clip` <[Object]> An object which specifies clipping region of the page. Should have the following fields:
|
|
- `x` <[number]> x-coordinate of top-left corner of clip area
|
|
- `y` <[number]> y-coordinate of top-left corner of clip area
|
|
- `width` <[number]> width of clipping area
|
|
- `height` <[number]> height of clipping area
|
|
- `omitBackground` <[boolean]> Hides default white background and allows capturing screenshots with transparency. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `encoding` <[string]> The encoding of the image, can be either `base64` or `binary`. Defaults to `binary`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Buffer|String]>> Promise which resolves to buffer or a base64 string (depending on the value of `encoding`) with captured screenshot.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Screenshots take at least 1/6 second on OS X. See https://crbug.com/741689 for discussion.
|
|
|
|
#### page.select(selector, ...values)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- `...values` <...[string]> Values of options to select. If the `<select>` has the `multiple` attribute, all values are considered, otherwise only the first one is taken into account.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[string]>>> Returns an array of option values that have been successfully selected.
|
|
|
|
Triggers a `change` and `input` event once all the provided options have been selected.
|
|
If there's no `<select>` element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.select('select#colors', 'blue'); // single selection
|
|
page.select('select#colors', 'red', 'green', 'blue'); // multiple selections
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().select()](#frameselectselector-values)
|
|
|
|
#### page.setBypassCSP(enabled)
|
|
- `enabled` <[boolean]> sets bypassing of page's Content-Security-Policy.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Toggles bypassing page's Content-Security-Policy.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** CSP bypassing happens at the moment of CSP initialization rather then evaluation. Usually this means
|
|
that `page.setBypassCSP` should be called before navigating to the domain.
|
|
|
|
#### page.setCacheEnabled(enabled)
|
|
- `enabled` <[boolean]> sets the `enabled` state of the cache.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Toggles ignoring cache for each request based on the enabled state. By default, caching is enabled.
|
|
|
|
#### page.setContent(html)
|
|
- `html` <[string]> HTML markup to assign to the page.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.setCookie(...cookies)
|
|
- `...cookies` <...[Object]>
|
|
- `name` <[string]> **required**
|
|
- `value` <[string]> **required**
|
|
- `url` <[string]>
|
|
- `domain` <[string]>
|
|
- `path` <[string]>
|
|
- `expires` <[number]> Unix time in seconds.
|
|
- `httpOnly` <[boolean]>
|
|
- `secure` <[boolean]>
|
|
- `sameSite` <[string]> `"Strict"` or `"Lax"`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds
|
|
|
|
This setting will change the default maximum navigation time of 30 seconds for the following methods:
|
|
- [page.goto(url, options)](#pagegotourl-options)
|
|
- [page.goBack(options)](#pagegobackoptions)
|
|
- [page.goForward(options)](#pagegoforwardoptions)
|
|
- [page.reload(options)](#pagereloadoptions)
|
|
- [page.waitForNavigation(options)](#pagewaitfornavigationoptions)
|
|
|
|
#### page.setExtraHTTPHeaders(headers)
|
|
- `headers` <[Object]> An object containing additional http headers to be sent with every request. All header values must be strings.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
The extra HTTP headers will be sent with every request the page initiates.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** page.setExtraHTTPHeaders does not guarantee the order of headers in the outgoing requests.
|
|
|
|
#### page.setJavaScriptEnabled(enabled)
|
|
- `enabled` <[boolean]> Whether or not to enable JavaScript on the page.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** changing this value won't affect scripts that have already been run. It will take full effect on the next [navigation](#pagegotourl-options).
|
|
|
|
#### page.setOfflineMode(enabled)
|
|
- `enabled` <[boolean]> When `true`, enables offline mode for the page.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.setRequestInterception(value)
|
|
- `value` <[boolean]> Whether to enable request interception.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Activating request interception enables `request.abort`, `request.continue` and
|
|
`request.respond` methods. This provides the capability to modify network requests that are made by a page.
|
|
|
|
An example of a naïve request interceptor that aborts all image requests:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
|
|
page.on('request', interceptedRequest => {
|
|
if (interceptedRequest.url().endsWith('.png') || interceptedRequest.url().endsWith('.jpg'))
|
|
interceptedRequest.abort();
|
|
else
|
|
interceptedRequest.continue();
|
|
});
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Enabling request interception disables page caching.
|
|
|
|
#### page.setUserAgent(userAgent)
|
|
- `userAgent` <[string]> Specific user agent to use in this page
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the user agent is set.
|
|
|
|
#### page.setViewport(viewport)
|
|
- `viewport` <[Object]>
|
|
- `width` <[number]> page width in pixels.
|
|
- `height` <[number]> page height in pixels.
|
|
- `deviceScaleFactor` <[number]> Specify device scale factor (can be thought of as dpr). Defaults to `1`.
|
|
- `isMobile` <[boolean]> Whether the `meta viewport` tag is taken into account. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hasTouch`<[boolean]> Specifies if viewport supports touch events. Defaults to `false`
|
|
- `isLandscape` <[boolean]> Specifies if viewport is in landscape mode. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** in certain cases, setting viewport will reload the page in order to set the `isMobile` or `hasTouch` properties.
|
|
|
|
In the case of multiple pages in a single browser, each page can have its own viewport size.
|
|
|
|
#### page.tap(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to tap. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be tapped.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.touchscreen](#pagetouchscreen) to tap in the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().tap(selector)](#frametapselector).
|
|
|
|
#### page.target()
|
|
- returns: <[Target]> a target this page was created from.
|
|
|
|
#### page.title()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[string]>> Returns page's title.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().title()](#frametitle).
|
|
|
|
#### page.touchscreen
|
|
- returns: <[Touchscreen]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.tracing
|
|
- returns: <[Tracing]>
|
|
|
|
#### page.type(selector, text[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to type into. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be used.
|
|
- `text` <[string]> A text to type into a focused element.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between key presses in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Sends a `keydown`, `keypress`/`input`, and `keyup` event for each character in the text.
|
|
|
|
To press a special key, like `Control` or `ArrowDown`, use [`keyboard.press`](#keyboardpresskey-options).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.type('#mytextarea', 'Hello'); // Types instantly
|
|
page.type('#mytextarea', 'World', {delay: 100}); // Types slower, like a user
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().type(selector, text[, options])](#frametypeselector-text-options).
|
|
|
|
#### page.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
This is a shortcut for [page.mainFrame().url()](#frameurl)
|
|
|
|
#### page.viewport()
|
|
- returns: <[Object]>
|
|
- `width` <[number]> page width in pixels.
|
|
- `height` <[number]> page height in pixels.
|
|
- `deviceScaleFactor` <[number]> Specify device scale factor (can be though of as dpr). Defaults to `1`.
|
|
- `isMobile` <[boolean]> Whether the `meta viewport` tag is taken into account. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hasTouch`<[boolean]> Specifies if viewport supports touch events. Defaults to `false`
|
|
- `isLandscape` <[boolean]> Specifies if viewport is in landscape mode. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
|
|
#### page.waitFor(selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout[, options[, ...args]])
|
|
- `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` <[string]|[number]|[function]> A [selector], predicate or timeout to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to a JSHandle of the success value
|
|
|
|
This method behaves differently with respect to the type of the first parameter:
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `string`, then the first argument is treated as a [selector] or [xpath], depending on whether or not it starts with '//', and the method is a shortcut for
|
|
[page.waitForSelector](#pagewaitforselectorselector-options) or [page.waitForXPath](#pagewaitforxpathxpath-options)
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `function`, then the first argument is treated as a predicate to wait for and the method is a shortcut for [page.waitForFunction()](#pagewaitforfunctionpagefunction-options-args).
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `number`, then the first argument is treated as a timeout in milliseconds and the method returns a promise which resolves after the timeout
|
|
- otherwise, an exception is thrown
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().waitFor(selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout[, options[, ...args]])](#framewaitforselectororfunctionortimeout-options-args).
|
|
|
|
#### page.waitForFunction(pageFunction[, options[, ...args]])
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `polling` <[string]|[number]> An interval at which the `pageFunction` is executed, defaults to `raf`. If `polling` is a number, then it is treated as an interval in milliseconds at which the function would be executed. If `polling` is a string, then it can be one of the following values:
|
|
- `raf` - to constantly execute `pageFunction` in `requestAnimationFrame` callback. This is the tightest polling mode which is suitable to observe styling changes.
|
|
- `mutation` - to execute `pageFunction` on every DOM mutation.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves when the `pageFunction` returns a truthy value. It resolves to a JSHandle of the truthy value.
|
|
|
|
The `waitForFunction` can be used to observe viewport size change:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
const watchDog = page.waitForFunction('window.innerWidth < 100');
|
|
await page.setViewport({width: 50, height: 50});
|
|
await watchDog;
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().waitForFunction(pageFunction[, options[, ...args]])](#framewaitforfunctionpagefunction-options-args).
|
|
|
|
#### page.waitForNavigation(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Navigation parameters which might have the following properties:
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> Maximum navigation time in milliseconds, defaults to 30 seconds, pass `0` to disable timeout. The default value can be changed by using the [page.setDefaultNavigationTimeout(timeout)](#pagesetdefaultnavigationtimeouttimeout) method.
|
|
- `waitUntil` <[string]|[Array]<[string]>> When to consider navigation succeeded, defaults to `load`. Given an array of event strings, navigation is considered to be successful after all events have been fired. Events can be either:
|
|
- `load` - consider navigation to be finished when the `load` event is fired.
|
|
- `domcontentloaded` - consider navigation to be finished when the `DOMContentLoaded` event is fired.
|
|
- `networkidle0` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 0 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- `networkidle2` - consider navigation to be finished when there are no more than 2 network connections for at least `500` ms.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Response]>> Promise which resolves to the main resource response. In case of multiple redirects, the navigation will resolve with the response of the last redirect.
|
|
|
|
This resolves when the page navigates to a new URL or reloads. It is useful for when you run code
|
|
which will indirectly cause the page to navigate. Consider this example:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const navigationPromise = page.waitForNavigation();
|
|
await page.click('a.my-link'); // Clicking the link will indirectly cause a navigation
|
|
await navigationPromise; // The navigationPromise resolves after navigation has finished
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
**NOTE** Usage of the [History API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/History_API) to change the URL is considered a navigation.
|
|
|
|
#### page.waitForSelector(selector[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `visible` <[boolean]> wait for element to be present in DOM and to be visible, i.e. to not have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hidden` <[boolean]> wait for element to not be found in the DOM or to be hidden, i.e. have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves when element specified by selector string is added to DOM.
|
|
|
|
Wait for the `selector` to appear in page. If at the moment of calling
|
|
the method the `selector` already exists, the method will return
|
|
immediately. If the selector doesn't appear after the `timeout` milliseconds of waiting, the function will throw.
|
|
|
|
This method works across navigations:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
let currentURL;
|
|
page
|
|
.waitForSelector('img')
|
|
.then(() => console.log('First URL with image: ' + currentURL));
|
|
for (currentURL of ['https://example.com', 'https://google.com', 'https://bbc.com'])
|
|
await page.goto(currentURL);
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().waitForSelector(selector[, options])](#framewaitforselectorselector-options).
|
|
|
|
#### page.waitForXPath(xpath[, options])
|
|
- `xpath` <[string]> A [xpath] of an element to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `visible` <[boolean]> wait for element to be present in DOM and to be visible, i.e. to not have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hidden` <[boolean]> wait for element to not be found in the DOM or to be hidden, i.e. have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves when element specified by xpath string is added to DOM.
|
|
|
|
Wait for the `xpath` to appear in page. If at the moment of calling
|
|
the method the `xpath` already exists, the method will return
|
|
immediately. If the xpath doesn't appear after the `timeout` milliseconds of waiting, the function will throw.
|
|
|
|
This method works across navigations:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
let currentURL;
|
|
page
|
|
.waitForXPath('//img')
|
|
.then(() => console.log('First URL with image: ' + currentURL));
|
|
for (currentURL of ['https://example.com', 'https://google.com', 'https://bbc.com'])
|
|
await page.goto(currentURL);
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
Shortcut for [page.mainFrame().waitForXPath(xpath[, options])](#framewaitforxpathxpath-options).
|
|
|
|
#### page.workers()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Worker]>>
|
|
This method returns all of the dedicated [WebWorkers](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API) associated with the page.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** This does not contain ServiceWorkers
|
|
|
|
### class: Worker
|
|
|
|
The Worker class represents a [WebWorker](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API).
|
|
The events `workercreated` and `workerdestroyed` are emitted on the page object to signal the worker lifecycle.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.on('workercreated', worker => console.log('Worker created: ' + worker.url()));
|
|
page.on('workerdestroyed', worker => console.log('Worker destroyed: ' + worker.url()));
|
|
|
|
console.log('Current workers:');
|
|
for (const worker of page.workers())
|
|
console.log(' ' + worker.url());
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### worker.executionContext()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ExecutionContext]>>
|
|
|
|
#### worker.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
### class: Keyboard
|
|
|
|
Keyboard provides an api for managing a virtual keyboard. The high level api is [`keyboard.type`](#keyboardtypetext-options), which takes raw characters and generates proper keydown, keypress/input, and keyup events on your page.
|
|
|
|
For finer control, you can use [`keyboard.down`](#keyboarddownkey-options), [`keyboard.up`](#keyboardupkey), and [`keyboard.sendCharacter`](#keyboardsendcharacterchar) to manually fire events as if they were generated from a real keyboard.
|
|
|
|
An example of holding down `Shift` in order to select and delete some text:
|
|
```js
|
|
await page.keyboard.type('Hello World!');
|
|
await page.keyboard.press('ArrowLeft');
|
|
|
|
await page.keyboard.down('Shift');
|
|
for (let i = 0; i < ' World'.length; i++)
|
|
await page.keyboard.press('ArrowLeft');
|
|
await page.keyboard.up('Shift');
|
|
|
|
await page.keyboard.press('Backspace');
|
|
// Result text will end up saying 'Hello!'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
An example of pressing `A`
|
|
```js
|
|
await page.keyboard.down('Shift');
|
|
await page.keyboard.press('KeyA');
|
|
await page.keyboard.up('Shift');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** On MacOS, keyboard shortcuts like `⌘ A` -> Select All do not work. See [#1313](https://github.com/GoogleChrome/puppeteer/issues/1313)
|
|
|
|
#### keyboard.down(key[, options])
|
|
- `key` <[string]> Name of key to press, such as `ArrowLeft`. See [USKeyboardLayout] for a list of all key names.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `text` <[string]> If specified, generates an input event with this text.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `keydown` event.
|
|
|
|
If `key` is a single character and no modifier keys besides `Shift` are being held down, a `keypress`/`input` event will also generated. The `text` option can be specified to force an input event to be generated.
|
|
|
|
If `key` is a modifier key, `Shift`, `Meta`, `Control`, or `Alt`, subsequent key presses will be sent with that modifier active. To release the modifier key, use [`keyboard.up`](#keyboardupkey).
|
|
|
|
After the key is pressed once, subsequent calls to [`keyboard.down`](#keyboarddownkey-options) will have [repeat](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/KeyboardEvent/repeat) set to true. To release the key, use [`keyboard.up`](#keyboardupkey).
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Modifier keys DO influence `keyboard.down`. Holding down `Shift` will type the text in upper case.
|
|
|
|
#### keyboard.press(key[, options])
|
|
- `key` <[string]> Name of key to press, such as `ArrowLeft`. See [USKeyboardLayout] for a list of all key names.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `text` <[string]> If specified, generates an input event with this text.
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `keydown` and `keyup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
If `key` is a single character and no modifier keys besides `Shift` are being held down, a `keypress`/`input` event will also generated. The `text` option can be specified to force an input event to be generated.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Modifier keys DO effect `elementHandle.press`. Holding down `Shift` will type the text in upper case.
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [`keyboard.down`](#keyboarddownkey-options) and [`keyboard.up`](#keyboardupkey).
|
|
|
|
#### keyboard.sendCharacter(char)
|
|
- `char` <[string]> Character to send into the page.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `keypress` and `input` event. This does not send a `keydown` or `keyup` event.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.keyboard.sendCharacter('嗨');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Modifier keys DO NOT effect `keyboard.sendCharacter`. Holding down `Shift` will not type the text in upper case.
|
|
|
|
#### keyboard.type(text, options)
|
|
- `text` <[string]> A text to type into a focused element.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between key presses in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Sends a `keydown`, `keypress`/`input`, and `keyup` event for each character in the text.
|
|
|
|
To press a special key, like `Control` or `ArrowDown`, use [`keyboard.press`](#keyboardpresskey-options).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.keyboard.type('Hello'); // Types instantly
|
|
page.keyboard.type('World', {delay: 100}); // Types slower, like a user
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Modifier keys DO NOT effect `keyboard.type`. Holding down `Shift` will not type the text in upper case.
|
|
|
|
#### keyboard.up(key)
|
|
- `key` <[string]> Name of key to release, such as `ArrowLeft`. See [USKeyboardLayout] for a list of all key names.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `keyup` event.
|
|
|
|
### class: Mouse
|
|
|
|
#### mouse.click(x, y, [options])
|
|
- `x` <[number]>
|
|
- `y` <[number]>
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `mousedown` and `mouseup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Shortcut for [`mouse.move`](#mousemovex-y-options), [`mouse.down`](#mousedownoptions) and [`mouse.up`](#mouseupoptions).
|
|
|
|
#### mouse.down([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `mousedown` event.
|
|
|
|
#### mouse.move(x, y, [options])
|
|
- `x` <[number]>
|
|
- `y` <[number]>
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `steps` <[number]> defaults to 1. Sends intermediate `mousemove` events.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `mousemove` event.
|
|
|
|
#### mouse.up([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `mouseup` event.
|
|
|
|
### class: Touchscreen
|
|
|
|
#### touchscreen.tap(x, y)
|
|
- `x` <[number]>
|
|
- `y` <[number]>
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Dispatches a `touchstart` and `touchend` event.
|
|
|
|
### class: Tracing
|
|
|
|
You can use [`tracing.start`](#tracingstartoptions) and [`tracing.stop`](#tracingstop) to create a trace file which can be opened in Chrome DevTools or [timeline viewer](https://chromedevtools.github.io/timeline-viewer/).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
await page.tracing.start({path: 'trace.json'});
|
|
await page.goto('https://www.google.com');
|
|
await page.tracing.stop();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### tracing.start(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `path` <[string]> A path to write the trace file to.
|
|
- `screenshots` <[boolean]> captures screenshots in the trace.
|
|
- `categories` <[Array]<[string]>> specify custom categories to use instead of default.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Only one trace can be active at a time per browser.
|
|
|
|
#### tracing.stop()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Buffer]>> Promise which resolves to buffer with trace data.
|
|
|
|
### class: Dialog
|
|
|
|
[Dialog] objects are dispatched by page via the ['dialog'](#event-dialog) event.
|
|
|
|
An example of using `Dialog` class:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
page.on('dialog', async dialog => {
|
|
console.log(dialog.message());
|
|
await dialog.dismiss();
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
page.evaluate(() => alert('1'));
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### dialog.accept([promptText])
|
|
- `promptText` <[string]> A text to enter in prompt. Does not cause any effects if the dialog's `type` is not prompt.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the dialog has been accepted.
|
|
|
|
#### dialog.defaultValue()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> If dialog is prompt, returns default prompt value. Otherwise, returns empty string.
|
|
|
|
#### dialog.dismiss()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the dialog has been dismissed.
|
|
|
|
#### dialog.message()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> A message displayed in the dialog.
|
|
|
|
#### dialog.type()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Dialog's type, can be one of `alert`, `beforeunload`, `confirm` or `prompt`.
|
|
|
|
### class: ConsoleMessage
|
|
|
|
[ConsoleMessage] objects are dispatched by page via the ['console'](#event-console) event.
|
|
|
|
#### consoleMessage.args()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[JSHandle]>>
|
|
|
|
#### consoleMessage.text()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
#### consoleMessage.type()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
One of the following values: `'log'`, `'debug'`, `'info'`, `'error'`, `'warning'`, `'dir'`, `'dirxml'`, `'table'`, `'trace'`, `'clear'`, `'startGroup'`, `'startGroupCollapsed'`, `'endGroup'`, `'assert'`, `'profile'`, `'profileEnd'`, `'count'`, `'timeEnd'`.
|
|
|
|
### class: Frame
|
|
|
|
At every point of time, page exposes its current frame tree via the [page.mainFrame()](#pagemainframe) and [frame.childFrames()](#framechildframes) methods.
|
|
|
|
[Frame] object's lifecycle is controlled by three events, dispatched on the page object:
|
|
- ['frameattached'](#event-frameattached) - fired when the frame gets attached to the page. A Frame can be attached to the page only once.
|
|
- ['framenavigated'](#event-framenavigated) - fired when the frame commits navigation to a different URL.
|
|
- ['framedetached'](#event-framedetached) - fired when the frame gets detached from the page. A Frame can be detached from the page only once.
|
|
|
|
An example of dumping frame tree:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.goto('https://www.google.com/chrome/browser/canary.html');
|
|
dumpFrameTree(page.mainFrame(), '');
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
|
|
function dumpFrameTree(frame, indent) {
|
|
console.log(indent + frame.url());
|
|
for (let child of frame.childFrames())
|
|
dumpFrameTree(child, indent + ' ');
|
|
}
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> Selector to query page for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves to ElementHandle pointing to the frame element.
|
|
|
|
The method queries frame for the selector. If there's no such element within the frame, the method will resolve to `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.$$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> Selector to query page for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[ElementHandle]>>> Promise which resolves to ElementHandles pointing to the frame elements.
|
|
|
|
The method runs `document.querySelectorAll` within the frame. If no elements match the selector, the return value resolve to `[]`.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.$$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query frame for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `Array.from(document.querySelectorAll(selector))` within the frame and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `frame.$$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```js
|
|
const divsCounts = await frame.$$eval('div', divs => divs.length);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.$eval(selector, pageFunction[, ...args])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query frame for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `document.querySelector` within the frame and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`. If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `frame.$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```js
|
|
const searchValue = await frame.$eval('#search', el => el.value);
|
|
const preloadHref = await frame.$eval('link[rel=preload]', el => el.href);
|
|
const html = await frame.$eval('.main-container', e => e.outerHTML);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.$x(expression)
|
|
- `expression` <[string]> Expression to [evaluate](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Document/evaluate).
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[ElementHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method evaluates the XPath expression.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.addScriptTag(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL of a script to be added.
|
|
- `path` <[string]> Path to the JavaScript file to be injected into frame. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- `content` <[string]> Raw JavaScript content to be injected into frame.
|
|
- `type` <[string]> Script type. Use 'module' in order to load a Javascript ES6 module. See [script](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/script) for more details.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> which resolves to the added tag when the script's onload fires or when the script content was injected into frame.
|
|
|
|
Adds a `<script>` tag into the page with the desired url or content.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.addStyleTag(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `url` <[string]> URL of the `<link>` tag.
|
|
- `path` <[string]> Path to the CSS file to be injected into frame. If `path` is a relative path, then it is resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- `content` <[string]> Raw CSS content to be injected into frame.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> which resolves to the added tag when the stylesheet's onload fires or when the CSS content was injected into frame.
|
|
|
|
Adds a `<link rel="stylesheet">` tag into the page with the desired url or a `<style type="text/css">` tag with the content.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.childFrames()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Frame]>>
|
|
|
|
#### frame.click(selector[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to click. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be clicked.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `mousedown` and `mouseup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully clicked. The Promise will be rejected if there is no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to click in the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
Bear in mind that if `click()` triggers a navigation event and there's a separate `page.waitForNavigation()` promise to be resolved, you may end up with a race condition that yields unexpected results. The correct pattern for click and wait for navigation is the following:
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
const [response] = await Promise.all([
|
|
page.waitForNavigation(waitOptions),
|
|
frame.click(selector, clickOptions),
|
|
]);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.content()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[String]>>
|
|
|
|
Gets the full HTML contents of the frame, including the doctype.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `frame.evaluate` returns a [Promise], then `frame.evaluate` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `frame.evaluate` returns a non-[Serializable] value, then `frame.evaluate` resolves to `undefined`.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const result = await frame.evaluate(() => {
|
|
return Promise.resolve(8 * 7);
|
|
});
|
|
console.log(result); // prints "56"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
console.log(await frame.evaluate('1 + 2')); // prints "3"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[ElementHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `frame.evaluate`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const bodyHandle = await frame.$('body');
|
|
const html = await frame.evaluate(body => body.innerHTML, bodyHandle);
|
|
await bodyHandle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in the page context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction` as in-page object (JSHandle)
|
|
|
|
The only difference between `frame.evaluate` and `frame.evaluateHandle` is that `frame.evaluateHandle` returns in-page object (JSHandle).
|
|
|
|
If the function, passed to the `frame.evaluateHandle`, returns a [Promise], then `frame.evaluateHandle` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const aWindowHandle = await frame.evaluateHandle(() => Promise.resolve(window));
|
|
aWindowHandle; // Handle for the window object.
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await frame.evaluateHandle('document'); // Handle for the 'document'.
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[JSHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `frame.evaluateHandle`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await frame.evaluateHandle(() => document.body);
|
|
const resultHandle = await frame.evaluateHandle(body => body.innerHTML, aHandle);
|
|
console.log(await resultHandle.jsonValue());
|
|
await resultHandle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### frame.executionContext()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ExecutionContext]>> Execution context associated with this frame.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.focus(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to focus. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be focused.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully focused. The promise will be rejected if there is no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector` and focuses it.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.hover(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to hover. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be hovered.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element matching `selector` is successfully hovered. Promise gets rejected if there's no element matching `selector`.
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to hover over the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.isDetached()
|
|
- returns: <[boolean]>
|
|
|
|
Returns `true` if the frame has been detached, or `false` otherwise.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.name()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
Returns frame's name attribute as specified in the tag.
|
|
|
|
If the name is empty, returns the id attribute instead.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** This value is calculated once when the frame is created, and will not update if the attribute is changed later.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.parentFrame()
|
|
- returns: <?[Frame]> Returns parent frame, if any. Detached frames and main frames return `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.select(selector, ...values)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query frame for
|
|
- `...values` <...[string]> Values of options to select. If the `<select>` has the `multiple` attribute, all values are considered, otherwise only the first one is taken into account.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[string]>>> Returns an array of option values that have been successfully selected.
|
|
|
|
Triggers a `change` and `input` event once all the provided options have been selected.
|
|
If there's no `<select>` element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
frame.select('select#colors', 'blue'); // single selection
|
|
frame.select('select#colors', 'red', 'green', 'blue'); // multiple selections
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.setContent(html)
|
|
- `html` <[string]> HTML markup to assign to the page.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
#### frame.tap(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to search for element to tap. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be tapped.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
This method fetches an element with `selector`, scrolls it into view if needed, and then uses [page.touchscreen](#pagetouchscreen) to tap in the center of the element.
|
|
If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.title()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[string]>> Returns page's title.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.type(selector, text[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to type into. If there are multiple elements satisfying the selector, the first will be used.
|
|
- `text` <[string]> A text to type into a focused element.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between key presses in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Sends a `keydown`, `keypress`/`input`, and `keyup` event for each character in the text.
|
|
|
|
To press a special key, like `Control` or `ArrowDown`, use [`keyboard.press`](#keyboardpresskey-options).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
frame.type('#mytextarea', 'Hello'); // Types instantly
|
|
frame.type('#mytextarea', 'World', {delay: 100}); // Types slower, like a user
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
Returns frame's url.
|
|
|
|
#### frame.waitFor(selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout[, options[, ...args]])
|
|
- `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` <[string]|[number]|[function]> A [selector], predicate or timeout to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to a JSHandle of the success value
|
|
|
|
This method behaves differently with respect to the type of the first parameter:
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `string`, then the first argument is treated as a [selector] or [xpath], depending on whether or not it starts with '//', and the method is a shortcut for
|
|
[frame.waitForSelector](#framewaitforselectorselector-options) or [frame.waitForXPath](#framewaitforxpathxpath-options)
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `function`, then the first argument is treated as a predicate to wait for and the method is a shortcut for [frame.waitForFunction()](#framewaitforfunctionpagefunction-options-args).
|
|
- if `selectorOrFunctionOrTimeout` is a `number`, then the first argument is treated as a timeout in milliseconds and the method returns a promise which resolves after the timeout
|
|
- otherwise, an exception is thrown
|
|
|
|
#### frame.waitForFunction(pageFunction[, options[, ...args]])
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `polling` <[string]|[number]> An interval at which the `pageFunction` is executed, defaults to `raf`. If `polling` is a number, then it is treated as an interval in milliseconds at which the function would be executed. If `polling` is a string, then it can be one of the following values:
|
|
- `raf` - to constantly execute `pageFunction` in `requestAnimationFrame` callback. This is the tightest polling mode which is suitable to observe styling changes.
|
|
- `mutation` - to execute `pageFunction` on every DOM mutation.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves when the `pageFunction` returns a truthy value. It resolves to a JSHandle of the truthy value.
|
|
|
|
The `waitForFunction` can be used to observe viewport size change:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
const watchDog = page.mainFrame().waitForFunction('window.innerWidth < 100');
|
|
page.setViewport({width: 50, height: 50});
|
|
await watchDog;
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.waitForSelector(selector[, options])
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] of an element to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `visible` <[boolean]> wait for element to be present in DOM and to be visible, i.e. to not have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hidden` <[boolean]> wait for element to not be found in the DOM or to be hidden, i.e. have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves when element specified by selector string is added to DOM.
|
|
|
|
Wait for the `selector` to appear in page. If at the moment of calling
|
|
the method the `selector` already exists, the method will return
|
|
immediately. If the selector doesn't appear after the `timeout` milliseconds of waiting, the function will throw.
|
|
|
|
This method works across navigations:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
let currentURL;
|
|
page.mainFrame()
|
|
.waitForSelector('img')
|
|
.then(() => console.log('First URL with image: ' + currentURL));
|
|
for (currentURL of ['https://example.com', 'https://google.com', 'https://bbc.com'])
|
|
await page.goto(currentURL);
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### frame.waitForXPath(xpath[, options])
|
|
- `xpath` <[string]> A [xpath] of an element to wait for
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Optional waiting parameters
|
|
- `visible` <[boolean]> wait for element to be present in DOM and to be visible, i.e. to not have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `hidden` <[boolean]> wait for element to not be found in the DOM or to be hidden, i.e. have `display: none` or `visibility: hidden` CSS properties. Defaults to `false`.
|
|
- `timeout` <[number]> maximum time to wait for in milliseconds. Defaults to `30000` (30 seconds). Pass `0` to disable timeout.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves when element specified by xpath string is added to DOM.
|
|
|
|
Wait for the `xpath` to appear in page. If at the moment of calling
|
|
the method the `xpath` already exists, the method will return
|
|
immediately. If the xpath doesn't appear after the `timeout` milliseconds of waiting, the function will throw.
|
|
|
|
This method works across navigations:
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
let currentURL;
|
|
page.mainFrame()
|
|
.waitForXPath('//img')
|
|
.then(() => console.log('First URL with image: ' + currentURL));
|
|
for (currentURL of ['https://example.com', 'https://google.com', 'https://bbc.com'])
|
|
await page.goto(currentURL);
|
|
await browser.close();
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### class: ExecutionContext
|
|
|
|
The class represents a context for JavaScript execution. Examples of JavaScript contexts are:
|
|
- each [frame](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/iframe) has a separate execution context
|
|
- all kind of [workers](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Web_Workers_API) have their own contexts
|
|
|
|
#### executionContext.evaluate(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in `executionContext`
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `executionContext.evaluate` returns a [Promise], then `executionContext.evaluate` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const executionContext = await page.mainFrame().executionContext();
|
|
const result = await executionContext.evaluate(() => Promise.resolve(8 * 7));
|
|
console.log(result); // prints "56"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
console.log(await executionContext.evaluate('1 + 2')); // prints "3"
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[JSHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `executionContext.evaluate`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const oneHandle = await executionContext.evaluateHandle(() => 1);
|
|
const twoHandle = await executionContext.evaluateHandle(() => 2);
|
|
const result = await executionContext.evaluate((a, b) => a + b, oneHandle, twoHandle);
|
|
await oneHandle.dispose();
|
|
await twoHandle.dispose();
|
|
console.log(result); // prints '3'.
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### executionContext.evaluateHandle(pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]|[string]> Function to be evaluated in the `executionContext`
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction` as in-page object (JSHandle)
|
|
|
|
The only difference between `executionContext.evaluate` and `executionContext.evaluateHandle` is that `executionContext.evaluateHandle` returns in-page object (JSHandle).
|
|
|
|
If the function passed to the `executionContext.evaluateHandle` returns a [Promise], then `executionContext.evaluateHandle` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const context = await page.mainFrame().executionContext();
|
|
const aHandle = await context.evaluateHandle(() => Promise.resolve(self));
|
|
aHandle; // Handle for the global object.
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
A string can also be passed in instead of a function.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await context.evaluateHandle('1 + 2'); // Handle for the '3' object.
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
[JSHandle] instances can be passed as arguments to the `executionContext.evaluateHandle`:
|
|
```js
|
|
const aHandle = await context.evaluateHandle(() => document.body);
|
|
const resultHandle = await context.evaluateHandle(body => body.innerHTML, aHandle);
|
|
console.log(await resultHandle.jsonValue()); // prints body's innerHTML
|
|
await aHandle.dispose();
|
|
await resultHandle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### executionContext.frame()
|
|
- returns: <?[Frame]> Frame associated with this execution context.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Not every execution context is associated with a frame. For example, workers and extensions have execution contexts that are not associated with frames.
|
|
|
|
#### executionContext.queryObjects(prototypeHandle)
|
|
- `prototypeHandle` <[JSHandle]> A handle to the object prototype.
|
|
- returns: <[JSHandle]> A handle to an array of objects with this prototype
|
|
|
|
The method iterates the JavaScript heap and finds all the objects with the given prototype.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Create a Map object
|
|
await page.evaluate(() => window.map = new Map());
|
|
// Get a handle to the Map object prototype
|
|
const mapPrototype = await page.evaluateHandle(() => Map.prototype);
|
|
// Query all map instances into an array
|
|
const mapInstances = await page.queryObjects(mapPrototype);
|
|
// Count amount of map objects in heap
|
|
const count = await page.evaluate(maps => maps.length, mapInstances);
|
|
await mapInstances.dispose();
|
|
await mapPrototype.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### class: JSHandle
|
|
|
|
JSHandle represents an in-page JavaScript object. JSHandles can be created with the [page.evaluateHandle](#pageevaluatehandlepagefunction-args) method.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const windowHandle = await page.evaluateHandle(() => window);
|
|
// ...
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
JSHandle prevents the referenced JavaScript object being garbage collected unless the handle is [disposed](#jshandledispose). JSHandles are auto-disposed when their origin frame gets navigated or the parent context gets destroyed.
|
|
|
|
JSHandle instances can be used as arguments in [`page.$eval()`](#pageevalselector-pagefunction-args), [`page.evaluate()`](#pageevaluatepagefunction-args) and [`page.evaluateHandle`](#pageevaluatehandlepagefunction-args) methods.
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.asElement()
|
|
- returns: <?[ElementHandle]>
|
|
|
|
Returns either `null` or the object handle itself, if the object handle is an instance of [ElementHandle].
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.dispose()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the object handle is successfully disposed.
|
|
|
|
The `jsHandle.dispose` method stops referencing the element handle.
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.executionContext()
|
|
- returns: [ExecutionContext]
|
|
|
|
Returns execution context the handle belongs to.
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.getProperties()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Map]<[string], [JSHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method returns a map with property names as keys and JSHandle instances for the property values.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const handle = await page.evaluateHandle(() => ({window, document}));
|
|
const properties = await handle.getProperties();
|
|
const windowHandle = properties.get('window');
|
|
const documentHandle = properties.get('document');
|
|
await handle.dispose();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.getProperty(propertyName)
|
|
- `propertyName` <[string]> property to get
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>>
|
|
|
|
Fetches a single property from the referenced object.
|
|
|
|
#### jsHandle.jsonValue()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Object]>>
|
|
|
|
Returns a JSON representation of the object. If the object has a
|
|
[`toJSON`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/stringify#toJSON()_behavior)
|
|
function, it **will not be called**.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** The method will return an empty JSON object if the referenced object is not stringifiable. It will throw an error if the object has circular references.
|
|
|
|
### class: ElementHandle
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Class [ElementHandle] extends [JSHandle].
|
|
|
|
ElementHandle represents an in-page DOM element. ElementHandles can be created with the [page.$](#pageselector) method.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
|
|
|
|
puppeteer.launch().then(async browser => {
|
|
const page = await browser.newPage();
|
|
await page.goto('https://google.com');
|
|
const inputElement = await page.$('input[type=submit]');
|
|
await inputElement.click();
|
|
// ...
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
ElementHandle prevents DOM element from garbage collection unless the handle is [disposed](#elementhandledispose). ElementHandles are auto-disposed when their origin frame gets navigated.
|
|
|
|
ElementHandle instances can be used as arguments in [`page.$eval()`](#pageevalselector-pagefunction-args) and [`page.evaluate()`](#pageevaluatepagefunction-args) methods.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query element for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[ElementHandle]>>
|
|
|
|
The method runs `element.querySelector` within the page. If no element matches the selector, the return value resolve to `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.$$(selector)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query element for
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[ElementHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method runs `element.querySelectorAll` within the page. If no elements match the selector, the return value resolve to `[]`.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.$$eval(selector, pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `document.querySelectorAll` within the element and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`. If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `frame.$$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```html
|
|
<div class="feed">
|
|
<div class="tweet">Hello!</div>
|
|
<div class="tweet">Hi!</div>
|
|
</div>
|
|
```
|
|
```js
|
|
const feedHandle = await page.$('.feed');
|
|
expect(await feedHandle.$$eval('.tweet', nodes => nodes.map(n => n.innerText)).toEqual(['Hello!', 'Hi!']);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.$eval(selector, pageFunction, ...args)
|
|
- `selector` <[string]> A [selector] to query page for
|
|
- `pageFunction` <[function]> Function to be evaluated in browser context
|
|
- `...args` <...[Serializable]|[JSHandle]> Arguments to pass to `pageFunction`
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Serializable]>> Promise which resolves to the return value of `pageFunction`
|
|
|
|
This method runs `document.querySelector` within the element and passes it as the first argument to `pageFunction`. If there's no element matching `selector`, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
If `pageFunction` returns a [Promise], then `frame.$eval` would wait for the promise to resolve and return its value.
|
|
|
|
Examples:
|
|
```js
|
|
const tweetHandle = await page.$('.tweet');
|
|
expect(await tweetHandle.$eval('.like', node => node.innerText)).toBe('100');
|
|
expect(await tweetHandle.$eval('.retweets', node => node.innerText)).toBe('10');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.$x(expression)
|
|
- `expression` <[string]> Expression to [evaluate](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Document/evaluate).
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[ElementHandle]>> Promise which resolves to ElementHandle pointing to the frame element.
|
|
|
|
The method evaluates the XPath expression relative to the elementHandle. If there's no such element, the method will resolve to `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.asElement()
|
|
- returns: <[elementhandle]>
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.boundingBox()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Object]>>
|
|
- x <[number]> the x coordinate of the element in pixels.
|
|
- y <[number]> the y coordinate of the element in pixels.
|
|
- width <[number]> the width of the element in pixels.
|
|
- height <[number]> the height of the element in pixels.
|
|
|
|
This method returns the bounding box of the element (relative to the main frame), or `null` if the element is not visible.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.boxModel()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Object]>>
|
|
- content <[Array]<[Object]>> Content box, represented as an array of {x, y} points.
|
|
- padding <[Array]<[Object]>> Padding box, represented as an array of {x, y} points.
|
|
- border <[Array]<[Object]>> Border box, represented as an array of {x, y} points.
|
|
- margin <[Array]<[Object]>> Margin box, represented as an array of {x, y} points.
|
|
- width <[number]> Element's width.
|
|
- height <[number]> Element's height.
|
|
|
|
This method returns boxes of the element, or `null` if the element is not visible. Boxes are represented as an array of points; each Point is an object `{x, y}`. Box points are sorted clock-wise.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.click([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `button` <[string]> `left`, `right`, or `middle`, defaults to `left`.
|
|
- `clickCount` <[number]> defaults to 1. See [UIEvent.detail].
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `mousedown` and `mouseup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element is successfully clicked. Promise gets rejected if the element is detached from DOM.
|
|
|
|
This method scrolls element into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to click in the center of the element.
|
|
If the element is detached from DOM, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.contentFrame()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Frame]>> Resolves to the content frame for element handles referencing iframe nodes, or null otherwise
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.dispose()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element handle is successfully disposed.
|
|
|
|
The `elementHandle.dispose` method stops referencing the element handle.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.executionContext()
|
|
- returns: [ExecutionContext]
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.focus()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Calls [focus](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/HTMLElement/focus) on the element.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.getProperties()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Map]<[string], [JSHandle]>>>
|
|
|
|
The method returns a map with property names as keys and JSHandle instances for the property values.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const listHandle = await page.evaluateHandle(() => document.body.children);
|
|
const properties = await listHandle.getProperties();
|
|
const children = [];
|
|
for (const property of properties.values()) {
|
|
const element = property.asElement();
|
|
if (element)
|
|
children.push(element);
|
|
}
|
|
children; // holds elementHandles to all children of document.body
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.getProperty(propertyName)
|
|
- `propertyName` <[string]> property to get
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[JSHandle]>>
|
|
|
|
Fetches a single property from the objectHandle.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.hover()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element is successfully hovered.
|
|
|
|
This method scrolls element into view if needed, and then uses [page.mouse](#pagemouse) to hover over the center of the element.
|
|
If the element is detached from DOM, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.jsonValue()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Object]>>
|
|
|
|
Returns a JSON representation of the object. The JSON is generated by running [`JSON.stringify`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/stringify) on the object in page and consequent [`JSON.parse`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/parse) in puppeteer.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** The method will throw if the referenced object is not stringifiable.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.press(key[, options])
|
|
- `key` <[string]> Name of key to press, such as `ArrowLeft`. See [USKeyboardLayout] for a list of all key names.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `text` <[string]> If specified, generates an input event with this text.
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between `keydown` and `keyup` in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Focuses the element, and then uses [`keyboard.down`](#keyboarddownkey-options) and [`keyboard.up`](#keyboardupkey).
|
|
|
|
If `key` is a single character and no modifier keys besides `Shift` are being held down, a `keypress`/`input` event will also be generated. The `text` option can be specified to force an input event to be generated.
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Modifier keys DO effect `elementHandle.press`. Holding down `Shift` will type the text in upper case.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.screenshot([options])
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Same options as in [page.screenshot](#pagescreenshotoptions).
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Buffer]>> Promise which resolves to buffer with captured screenshot.
|
|
|
|
This method scrolls element into view if needed, and then uses [page.screenshot](#pagescreenshotoptions) to take a screenshot of the element.
|
|
If the element is detached from DOM, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.tap()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise which resolves when the element is successfully tapped. Promise gets rejected if the element is detached from DOM.
|
|
|
|
This method scrolls element into view if needed, and then uses [touchscreen.tap](#touchscreentapx-y) to tap in the center of the element.
|
|
If the element is detached from DOM, the method throws an error.
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.toString()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.type(text[, options])
|
|
- `text` <[string]> A text to type into a focused element.
|
|
- `options` <[Object]>
|
|
- `delay` <[number]> Time to wait between key presses in milliseconds. Defaults to 0.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Focuses the element, and then sends a `keydown`, `keypress`/`input`, and `keyup` event for each character in the text.
|
|
|
|
To press a special key, like `Control` or `ArrowDown`, use [`elementHandle.press`](#elementhandlepresskey-options).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
elementHandle.type('Hello'); // Types instantly
|
|
elementHandle.type('World', {delay: 100}); // Types slower, like a user
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
An example of typing into a text field and then submitting the form:
|
|
```js
|
|
const elementHandle = await page.$('input');
|
|
await elementHandle.type('some text');
|
|
await elementHandle.press('Enter');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### elementHandle.uploadFile(...filePaths)
|
|
- `...filePaths` <...[string]> Sets the value of the file input these paths. If some of the `filePaths` are relative paths, then they are resolved relative to [current working directory](https://nodejs.org/api/process.html#process_process_cwd).
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
This method expects `elementHandle` to point to an [input element](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/input).
|
|
|
|
### class: Request
|
|
|
|
Whenever the page sends a request, such as for a network resource, the following events are emitted by puppeteer's page:
|
|
- ['request'](#event-request) emitted when the request is issued by the page.
|
|
- ['response'](#event-response) emitted when/if the response is received for the request.
|
|
- ['requestfinished'](#event-requestfinished) emitted when the response body is downloaded and the request is complete.
|
|
|
|
If request fails at some point, then instead of 'requestfinished' event (and possibly instead of 'response' event), the ['requestfailed'](#event-requestfailed) event is emitted.
|
|
|
|
If request gets a 'redirect' response, the request is successfully finished with the 'requestfinished' event, and a new request is issued to a redirected url.
|
|
|
|
#### request.abort([errorCode])
|
|
- `errorCode` <[string]> Optional error code. Defaults to `failed`, could be
|
|
one of the following:
|
|
- `aborted` - An operation was aborted (due to user action)
|
|
- `accessdenied` - Permission to access a resource, other than the network, was denied
|
|
- `addressunreachable` - The IP address is unreachable. This usually means
|
|
that there is no route to the specified host or network.
|
|
- `connectionaborted` - A connection timed out as a result of not receiving an ACK for data sent.
|
|
- `connectionclosed` - A connection was closed (corresponding to a TCP FIN).
|
|
- `connectionfailed` - A connection attempt failed.
|
|
- `connectionrefused` - A connection attempt was refused.
|
|
- `connectionreset` - A connection was reset (corresponding to a TCP RST).
|
|
- `internetdisconnected` - The Internet connection has been lost.
|
|
- `namenotresolved` - The host name could not be resolved.
|
|
- `timedout` - An operation timed out.
|
|
- `failed` - A generic failure occurred.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Aborts request. To use this, request interception should be enabled with `page.setRequestInterception`.
|
|
Exception is immediately thrown if the request interception is not enabled.
|
|
|
|
#### request.continue([overrides])
|
|
- `overrides` <[Object]> Optional request overwrites, which can be one of the following:
|
|
- `url` <[string]> If set, the request url will be changed
|
|
- `method` <[string]> If set changes the request method (e.g. `GET` or `POST`)
|
|
- `postData` <[string]> If set changes the post data of request
|
|
- `headers` <[Object]> If set changes the request HTTP headers
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Continues request with optional request overrides. To use this, request interception should be enabled with `page.setRequestInterception`.
|
|
Exception is immediately thrown if the request interception is not enabled.
|
|
|
|
#### request.failure()
|
|
- returns: <?[Object]> Object describing request failure, if any
|
|
- `errorText` <[string]> Human-readable error message, e.g. `'net::ERR_FAILED'`.
|
|
|
|
The method returns `null` unless this request was failed, as reported by
|
|
`requestfailed` event.
|
|
|
|
Example of logging all failed requests:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
page.on('requestfailed', request => {
|
|
console.log(request.url() + ' ' + request.failure().errorText);
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### request.frame()
|
|
- returns: <?[Frame]> A matching [Frame] object, or `null` if navigating to error pages.
|
|
|
|
#### request.headers()
|
|
- returns: <[Object]> An object with HTTP headers associated with the request. All header names are lower-case.
|
|
|
|
#### request.method()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Request's method (GET, POST, etc.)
|
|
|
|
#### request.postData()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Request's post body, if any.
|
|
|
|
#### request.redirectChain()
|
|
- returns: <[Array]<[Request]>>
|
|
|
|
A `redirectChain` is a chain of requests initiated to fetch a resource.
|
|
- If there are no redirects and the request was successful, the chain will be empty.
|
|
- If a server responds with at least a single redirect, then the chain will
|
|
contain all the requests that were redirected.
|
|
|
|
`redirectChain` is shared between all the requests of the same chain.
|
|
|
|
For example, if the website `http://example.com` has a single redirect to
|
|
`https://example.com`, then the chain will contain one request:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const response = await page.goto('http://example.com');
|
|
const chain = response.request().redirectChain();
|
|
console.log(chain.length); // 1
|
|
console.log(chain[0].url()); // 'http://example.com'
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If the website `https://google.com` has no redirects, then the chain will be empty:
|
|
```js
|
|
const response = await page.goto('https://google.com');
|
|
const chain = response.request().redirectChain();
|
|
console.log(chain.length); // 0
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### request.resourceType()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
Contains the request's resource type as it was perceived by the rendering engine.
|
|
ResourceType will be one of the following: `document`, `stylesheet`, `image`, `media`, `font`, `script`, `texttrack`, `xhr`, `fetch`, `eventsource`, `websocket`, `manifest`, `other`.
|
|
|
|
#### request.respond(response)
|
|
- `response` <[Object]> Response that will fulfill this request
|
|
- `status` <[number]> Response status code, defaults to `200`.
|
|
- `headers` <[Object]> Optional response headers
|
|
- `contentType` <[string]> If set, equals to setting `Content-Type` response header
|
|
- `body` <[Buffer]|[string]> Optional response body
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Fulfills request with given response. To use this, request interception should
|
|
be enabled with `page.setRequestInterception`. Exception is thrown if
|
|
request interception is not enabled.
|
|
|
|
An example of fulfilling all requests with 404 responses:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
|
|
page.on('request', request => {
|
|
request.respond({
|
|
status: 404,
|
|
contentType: 'text/plain',
|
|
body: 'Not Found!'
|
|
});
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** Mocking responses for dataURL requests is not supported.
|
|
> Calling `request.respond` for a dataURL request is a noop.
|
|
|
|
#### request.response()
|
|
- returns: <?[Response]> A matching [Response] object, or `null` if the response has not been received yet.
|
|
|
|
#### request.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> URL of the request.
|
|
|
|
### class: Response
|
|
|
|
[Response] class represents responses which are received by page.
|
|
|
|
#### response.buffer()
|
|
- returns: <Promise<[Buffer]>> Promise which resolves to a buffer with response body.
|
|
|
|
#### response.fromCache()
|
|
- returns: <[boolean]>
|
|
|
|
True if the response was served from either the browser's disk cache or memory cache.
|
|
|
|
#### response.fromServiceWorker()
|
|
- returns: <[boolean]>
|
|
|
|
True if the response was served by a service worker.
|
|
|
|
#### response.headers()
|
|
- returns: <[Object]> An object with HTTP headers associated with the response. All header names are lower-case.
|
|
|
|
#### response.json()
|
|
- returns: <Promise<[Object]>> Promise which resolves to a JSON representation of response body.
|
|
|
|
This method will throw if the response body is not parsable via `JSON.parse`.
|
|
|
|
#### response.ok()
|
|
- returns: <[boolean]>
|
|
|
|
Contains a boolean stating whether the response was successful (status in the range 200-299) or not.
|
|
|
|
#### response.request()
|
|
- returns: <[Request]> A matching [Request] object.
|
|
|
|
#### response.securityDetails()
|
|
- returns: <?[SecurityDetails]> Security details if the response was received over the secure connection, or `null` otherwise.
|
|
|
|
#### response.status()
|
|
- returns: <[number]>
|
|
|
|
Contains the status code of the response (e.g., 200 for a success).
|
|
|
|
#### response.text()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[string]>> Promise which resolves to a text representation of response body.
|
|
|
|
#### response.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
Contains the URL of the response.
|
|
|
|
### class: SecurityDetails
|
|
|
|
[SecurityDetails] class represents responses which are received by page.
|
|
|
|
#### securityDetails.issuer()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> A string with the name of issuer of the certificate.
|
|
|
|
#### securityDetails.protocol()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> String with the security protocol, eg. "TLS 1.2".
|
|
|
|
#### securityDetails.subjectName()
|
|
- returns: <[string]> Name of the subject to which the certificate was issued to.
|
|
|
|
#### securityDetails.validFrom()
|
|
- returns: <[number]> [UnixTime] stating the start of validity of the certificate.
|
|
|
|
#### securityDetails.validTo()
|
|
- returns: <[number]> [UnixTime] stating the end of validity of the certificate.
|
|
|
|
### class: Target
|
|
|
|
#### target.browser()
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[Browser]>
|
|
|
|
Get the browser the target belongs to.
|
|
|
|
#### target.browserContext()
|
|
|
|
- returns: <[BrowserContext]>
|
|
|
|
The browser context the target belongs to.
|
|
|
|
#### target.createCDPSession()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[CDPSession]>>
|
|
|
|
Creates a Chrome Devtools Protocol session attached to the target.
|
|
|
|
#### target.page()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<?[Page]>>
|
|
|
|
If the target is not of type `"page"`, returns `null`.
|
|
|
|
#### target.type()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
Identifies what kind of target this is. Can be `"page"`, [`"background_page"`](https://developer.chrome.com/extensions/background_pages), `"service_worker"`, `"browser"` or `"other"`.
|
|
|
|
#### target.url()
|
|
- returns: <[string]>
|
|
|
|
### class: CDPSession
|
|
|
|
* extends: [`EventEmitter`](https://nodejs.org/api/events.html#events_class_eventemitter)
|
|
|
|
The `CDPSession` instances are used to talk raw Chrome Devtools Protocol:
|
|
- protocol methods can be called with `session.send` method.
|
|
- protocol events can be subscribed to with `session.on` method.
|
|
|
|
Documentation on DevTools Protocol can be found here: [DevTools Protocol Viewer](https://chromedevtools.github.io/devtools-protocol/).
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const client = await page.target().createCDPSession();
|
|
await client.send('Animation.enable');
|
|
await client.on('Animation.animationCreated', () => console.log('Animation created!'));
|
|
const response = await client.send('Animation.getPlaybackRate');
|
|
console.log('playback rate is ' + response.playbackRate);
|
|
await client.send('Animation.setPlaybackRate', {
|
|
playbackRate: response.playbackRate / 2
|
|
});
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
#### cdpSession.detach()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]>
|
|
|
|
Detaches the cdpSession from the target. Once detached, the cdpSession object won't emit any events and can't be used
|
|
to send messages.
|
|
|
|
#### cdpSession.send(method[, params])
|
|
- `method` <[string]> protocol method name
|
|
- `params` <[Object]> Optional method parameters
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Object]>>
|
|
|
|
### class: Coverage
|
|
|
|
Coverage gathers information about parts of JavaScript and CSS that were used by the page.
|
|
|
|
An example of using JavaScript and CSS coverage to get percentage of initially
|
|
executed code:
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Enable both JavaScript and CSS coverage
|
|
await Promise.all([
|
|
page.coverage.startJSCoverage(),
|
|
page.coverage.startCSSCoverage()
|
|
]);
|
|
// Navigate to page
|
|
await page.goto('https://example.com');
|
|
// Disable both JavaScript and CSS coverage
|
|
const [jsCoverage, cssCoverage] = await Promise.all([
|
|
page.coverage.stopJSCoverage(),
|
|
page.coverage.stopCSSCoverage(),
|
|
]);
|
|
let totalBytes = 0;
|
|
let usedBytes = 0;
|
|
const coverage = [...jsCoverage, ...cssCoverage];
|
|
for (const entry of coverage) {
|
|
totalBytes += entry.text.length;
|
|
for (const range of entry.ranges)
|
|
usedBytes += range.end - range.start - 1;
|
|
}
|
|
console.log(`Bytes used: ${usedBytes / totalBytes * 100}%`);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
_To output coverage in a form consumable by [Istanbul](https://github.com/istanbuljs),
|
|
see [puppeteer-to-istanbul](https://github.com/istanbuljs/puppeteer-to-istanbul)._
|
|
|
|
#### coverage.startCSSCoverage(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Set of configurable options for coverage
|
|
- `resetOnNavigation` <[boolean]> Whether to reset coverage on every navigation. Defaults to `true`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise that resolves when coverage is started
|
|
|
|
#### coverage.startJSCoverage(options)
|
|
- `options` <[Object]> Set of configurable options for coverage
|
|
- `resetOnNavigation` <[boolean]> Whether to reset coverage on every navigation. Defaults to `true`.
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]> Promise that resolves when coverage is started
|
|
|
|
#### coverage.stopCSSCoverage()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[Object]>>> Promise that resolves to the array of coverage reports for all stylesheets
|
|
- `url` <[string]> StyleSheet URL
|
|
- `text` <[string]> StyleSheet content
|
|
- `ranges` <[Array]<[Object]>> StyleSheet ranges that were used. Ranges are sorted and non-overlapping.
|
|
- `start` <[number]> A start offset in text, inclusive
|
|
- `end` <[number]> An end offset in text, exclusive
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** CSS Coverage doesn't include dynamically injected style tags without sourceURLs.
|
|
|
|
#### coverage.stopJSCoverage()
|
|
- returns: <[Promise]<[Array]<[Object]>>> Promise that resolves to the array of coverage reports for all non-anonymous scripts
|
|
- `url` <[string]> Script URL
|
|
- `text` <[string]> Script content
|
|
- `ranges` <[Array]<[Object]>> Script ranges that were executed. Ranges are sorted and non-overlapping.
|
|
- `start` <[number]> A start offset in text, inclusive
|
|
- `end` <[number]> An end offset in text, exclusive
|
|
|
|
> **NOTE** JavaScript Coverage doesn't include anonymous scripts. However, scripts with sourceURLs are
|
|
reported.
|
|
|
|
[Array]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array "Array"
|
|
[boolean]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Data_structures#Boolean_type "Boolean"
|
|
[Buffer]: https://nodejs.org/api/buffer.html#buffer_class_buffer "Buffer"
|
|
[function]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Function "Function"
|
|
[number]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Data_structures#Number_type "Number"
|
|
[Object]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object "Object"
|
|
[Page]: #class-page "Page"
|
|
[Promise]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Promise "Promise"
|
|
[string]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Data_structures#String_type "String"
|
|
[stream.Readable]: https://nodejs.org/api/stream.html#stream_class_stream_readable "stream.Readable"
|
|
[CDPSession]: #class-cdpsession "CDPSession"
|
|
[BrowserFetcher]: #class-browserfetcher "BrowserFetcher"
|
|
[BrowserContext]: #class-browsercontext "BrowserContext"
|
|
[Error]: https://nodejs.org/api/errors.html#errors_class_error "Error"
|
|
[Frame]: #class-frame "Frame"
|
|
[ConsoleMessage]: #class-consolemessage "ConsoleMessage"
|
|
[ChildProcess]: https://nodejs.org/api/child_process.html "ChildProcess"
|
|
[Coverage]: #class-coverage "Coverage"
|
|
[iterator]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Iteration_protocols "Iterator"
|
|
[Response]: #class-response "Response"
|
|
[Request]: #class-request "Request"
|
|
[Browser]: #class-browser "Browser"
|
|
[Body]: #class-body "Body"
|
|
[Element]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/element "Element"
|
|
[Keyboard]: #class-keyboard "Keyboard"
|
|
[Dialog]: #class-dialog "Dialog"
|
|
[JSHandle]: #class-jshandle "JSHandle"
|
|
[ExecutionContext]: #class-executioncontext "ExecutionContext"
|
|
[Mouse]: #class-mouse "Mouse"
|
|
[Map]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Map "Map"
|
|
[selector]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Selectors "selector"
|
|
[Tracing]: #class-tracing "Tracing"
|
|
[ElementHandle]: #class-elementhandle "ElementHandle"
|
|
[UIEvent.detail]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/UIEvent/detail "UIEvent.detail"
|
|
[Serializable]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/stringify#Description "Serializable"
|
|
[Touchscreen]: #class-touchscreen "Touchscreen"
|
|
[Target]: #class-target "Target"
|
|
[USKeyboardLayout]: ../lib/USKeyboardLayout.js "USKeyboardLayout"
|
|
[xpath]: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/XPath "xpath"
|
|
[UnixTime]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unix_time "Unix Time"
|
|
[SecurityDetails]: #class-securitydetails "SecurityDetails"
|
|
[Worker]: #class-worker "Worker"
|